Network address translation facts for kids
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a clever way computers on a network share one main internet address. Think of it like a big apartment building that has one main street address, but many apartments inside. NAT helps many devices, like your phone, computer, and tablet, all use the internet at the same time through your home router.
This technology is super important because there aren't enough unique internet addresses (called IP addresses) for every single device in the world, especially with the older system called IPv4. NAT helps solve this problem by letting many devices use just one public IP address.
NAT also helps keep your home network private. It hides the specific addresses of your devices from the outside internet. This is sometimes called "network masquerading" or "IP masquerading" because it makes it look like all your devices are just one device to the rest of the internet.
Contents
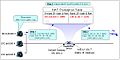
How NAT Works
NAT usually happens inside your router. Your router is like a traffic cop for your internet connection. When you send information from your computer to the internet, the router changes your computer's private address to the router's public address. When the internet sends information back, the router knows which of your devices it's meant for and sends it to the correct one.
NAT's Translation Table
The router uses a special list, like a phone book, called a "translation table." This table helps the router remember which private address belongs to which internet request. When your computer asks for a webpage, the router adds a note to this table. When the webpage comes back, the router looks at its table to send the information to your computer.
These notes in the table usually disappear after a short time if they aren't used. But, sometimes, network experts can set up permanent notes in the table. This is called "static NAT" or port forwarding. It lets people on the internet reach specific devices inside your private network, which is useful for things like online gaming servers.
Different Kinds of NAT
Carrier-Grade NAT
Sometimes, even big internet companies (called Internet Service Providers or ISPs) don't have enough IP addresses for all their customers. They use something called Carrier-Grade NAT (CGN). This is like a super-sized NAT that helps many customers share a smaller number of public IP addresses. You might see this used by mobile phone companies for 3G and 4G networks.
NAT and IPv6
NAT is mostly used with the older IPv4 system. However, a newer internet address system called IPv6 has a huge number of addresses. There are so many IPv6 addresses that every device in the world could have its own unique address, and there would still be plenty left over! Because of this, NAT is not needed for IPv6.
Related pages
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Traducción de direcciones de red para niños
In Spanish: Traducción de direcciones de red para niños