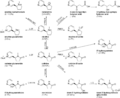Nicotine facts for kids
Nicotine is a chemical found in tobacco plants. It is in products like cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco, and chewing tobacco. Nicotine is a stimulant, which means it speeds up your body. It makes your heart beat faster and raises your blood pressure. It can also make you feel less hungry. These effects can be unhealthy. Many people who use tobacco want to quit but find it very hard. Nicotine is one of the most addictive chemicals people use.
Small amounts of nicotine are also found in other plants. These include tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, and green peppers. Nicotine is also in the coca plant. In large amounts, nicotine is a strong poison. It affects your nerves. In smaller amounts, it acts as a stimulant. It is a main reason why people get addicted to smoking.
Nicotine gets its name from Jean Nicot. He was a French ambassador in Portugal. He sent tobacco seeds to Paris for study.
Besides helping people stop using tobacco, nicotine might also help with some types of epilepsy. It may also help with other health problems.
Contents
Nicotine in Cigarettes
The amount of nicotine in one cigarette can be very different. This depends on the type of tobacco used. It also depends on the cigarette brand. Different countries may have rules about nicotine levels. How a person smokes the cigarette also changes the amount.
How Nicotine Affects Your Body
Nicotine is known as a poison. In small amounts, it can slightly reduce pain. But in larger amounts, nicotine can cause problems. These include feeling sick to your stomach, throwing up, or having diarrhea. It can also cause dizziness, headaches, and trouble sleeping.
Here are some common effects of nicotine use:
- For gums and lozenges: Upset stomach, hiccups, sore mouth, and headaches.
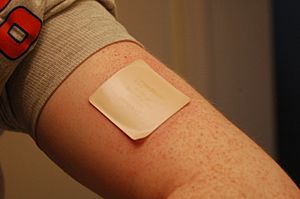
- For patches: Skin irritation where the patch is, upset stomach, and vivid dreams.
- For nasal sprays: Runny nose, watery eyes, and sneezing.
- For inhalers: Upset stomach and irritation in the mouth and throat.
- Overall effects: Faster heart rate, higher blood pressure, and increased alertness.
Sleep
Nicotine can make it harder to get good sleep. It reduces the amount of deep sleep you get. It also reduces your total sleep time. The more nicotine used, the more it affects your sleep.
Heart and Blood
Nicotine can temporarily raise your blood pressure. However, long-term studies do not usually show high blood pressure in people who use nicotine. For people with heart problems, nicotine from e-cigarettes might cause some risk.
Addiction
Nicotine is very addictive. This means it is hard to stop using it once you start. People can become both mentally and physically dependent on it. When someone stops using nicotine, they might feel anxious or irritable. They might also have cravings or mild shaking. These feelings are called withdrawal symptoms. They can be strongest for a few days. Some people feel them for several weeks or even longer.
Cancer
Nicotine can help lung cancer grow faster. It can also make cancer cells harder to treat with medicines.
Cell Damage
Nicotine can damage the DNA in human cells. DNA is like the instruction manual for your body's cells.
During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Nicotine can harm unborn babies. It can cause problems with how the baby's brain develops. It can also lead to issues during pregnancy and birth. Pregnant women who smoke have a higher risk of miscarriage or stillbirth. Babies exposed to nicotine before birth often have lower birth weights. Nicotine can pass from the mother to the baby during pregnancy. It can also be found in breast milk.
Studies in animals show that nicotine exposure before birth can lead to health problems later in life. These can include conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Nicotina para niños
In Spanish: Nicotina para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |