Nonvolatile BIOS memory facts for kids
A small memory on your computer's motherboard is called Nonvolatile BIOS memory. It stores important settings for your computer's basic software, called the BIOS. People often call it CMOS RAM. This is because it uses a special low-power technology called CMOS (complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor).
This memory needs a small "CMOS" battery to keep its settings when your computer is turned off or unplugged. Because it keeps its information even without main power, it's known as non-volatile memory. It usually holds about 256 bytes of data.
In modern computers, the CMOS RAM and the real-time clock are often built into a larger chip on the motherboard. This chip is usually part of the Platform Controller Hub.
Newer computers use UEFI instead of BIOS. They store settings in a different type of NVRAM within the UEFI flash memory. However, if the CMOS battery dies, these UEFI settings can still be lost.
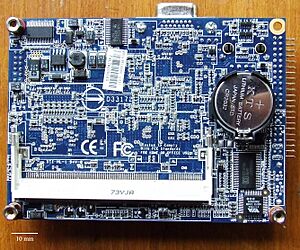
The CMOS Battery
The memory battery is also known as the motherboard, CMOS, or real-time clock (RTC) battery. It is usually a CR2032 lithium coin cell. This battery can last about three years if your computer's power supply is unplugged.
Unlike lithium-ion batteries, this type of battery cannot be recharged. Trying to recharge it could be dangerous. Motherboards have special parts that stop these batteries from charging when the computer is on.
Other battery types might last longer or shorter. For example, a smaller CR2016 battery usually lasts about 40% less time than a CR2032. Hotter temperatures and longer times with no power can make the battery die faster.
When you replace the battery, your computer's time and BIOS settings might go back to their original factory settings. To avoid this, you can replace the battery while the computer is plugged into power and the power switch is on. On ATX motherboards, the power supply keeps a small amount of power flowing to the motherboard. This helps keep the CMOS memory working even when the computer is off.
Some older computers used different types of batteries. These included cylindrical "1/2 AA" batteries or "barrel-shaped" nickel–cadmium (Ni–Cd) batteries. Ni–Cd batteries can sometimes leak over time, which can damage parts of the circuit board near the battery.
See also
 In Spanish: RAM-CMOS para niños
In Spanish: RAM-CMOS para niños
- Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD)
- List of battery types