Nucleobase facts for kids
Nucleobases are super important tiny parts inside your body that help make up your DNA and RNA. Think of them as special building blocks that carry all the instructions for how you grow and work! They are often just called bases for short.
Contents
What Are Nucleobases?
Nucleobases are special chemical compounds. They are a key part of the larger molecules called nucleotides. Nucleotides then link together to form the long chains of DNA and RNA. These chains hold all the genetic information in living things.
The Main Types of Nucleobases
There are five main types of nucleobases that you'll hear about:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)
- Uracil (U)
You can remember them by their first letters: A, G, C, T, and U.
Nucleobases in DNA and RNA
DNA and RNA are two different types of genetic material. They use slightly different sets of nucleobases:
- In DNA, you will find Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Thymine (T). These are often called DNA-bases.
- In RNA, you will find Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), and Uracil (U). These are called RNA-bases.
Notice that Uracil (U) takes the place of Thymine (T) in RNA.
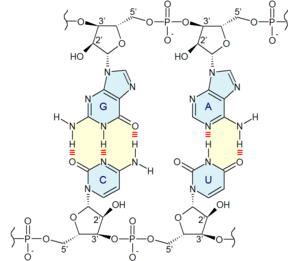
How Nucleobases Pair Up
One of the most amazing things about nucleobases is how they pair up with each other. This pairing is called base pairing and it's essential for how DNA and RNA work.
- Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T) in DNA.
- Adenine (A) always pairs with Uracil (U) in RNA.
- Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C) in both DNA and RNA.
These pairs are like puzzle pieces that fit together perfectly. This special pairing helps DNA make copies of itself and helps RNA carry out its jobs in the cell.
Why Are Nucleobases Important?
Nucleobases are the core of our genetic code. They are like the letters in a secret instruction manual for life. The order of these bases along the DNA and RNA strands tells our bodies how to build proteins, which are the tiny machines that do almost everything in our cells. Without nucleobases, life as we know it wouldn't exist!
See also
 In Spanish: Nucleobase para niños
In Spanish: Nucleobase para niños
 | Laphonza Butler |
 | Daisy Bates |
 | Elizabeth Piper Ensley |