Operating reserve facts for kids
An electrical grid is a huge network that brings electricity from power plants to homes and businesses. Sometimes, things can go wrong, like a power plant suddenly stopping or many people turning on their air conditioners at once. When this happens, the grid needs a quick backup plan to avoid a power outage. This backup plan is called operating reserve. It's the extra power that can be quickly added to the grid to keep the lights on and prevent a long power shortage.
Contents
What is Operating Reserve?
Operating reserve is like a safety net for the electricity system. It's the extra power that power plants can produce very quickly if needed. Imagine a busy highway: if one lane suddenly closes, you need other lanes to handle the traffic. Operating reserve does the same for electricity. It makes sure there's always enough power, even if something unexpected happens.
Why Do We Need Operating Reserve?
The demand for electricity changes all the time. More power is needed during the day when people are at work or school, and less at night. Also, power plants can sometimes break down unexpectedly. If the power supply doesn't match the demand, the entire electrical grid can become unstable. This can lead to widespread power outages, which means no electricity for homes, hospitals, or traffic lights. Operating reserve helps prevent these problems by providing a fast way to balance the supply and demand of electricity.
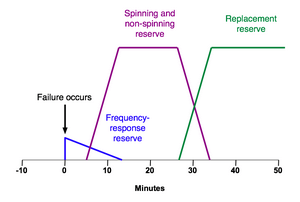
Types of Operating Reserve
Operating reserve is usually split into two main types: spinning reserve and non-spinning reserve. Both are important for keeping the grid stable, but they work in slightly different ways.
Spinning Reserve
Spinning reserve is power that is already being produced or can be produced almost instantly. Think of it as power plants that are already running and connected to the grid. They might be producing some electricity, but they have extra capacity ready to go. If there's a sudden need for more power, these plants can quickly increase their output. They are "spinning" and ready to deliver more power in seconds. This type of reserve is the fastest to respond.
Non-Spinning Reserve
Non-spinning reserve is power that can be brought online very quickly, but not instantly. These are often power plants that are not currently running but can be started up in a few minutes. Or, it could be power from sources that are not connected to the grid yet but can be connected fast. While not as immediate as spinning reserve, non-spinning reserve is still crucial for handling larger or longer-lasting power needs. It acts as the next layer of backup.
How Does It Work?
Grid operators, who manage the electrical system, constantly monitor the power supply and demand. They use special equipment to detect any sudden changes. If a power plant fails or demand suddenly jumps, the operators quickly activate the operating reserve. This means telling the power plants with reserve capacity to increase their output. This quick response helps to keep the frequency of the electricity stable. Keeping the frequency stable is vital for all electrical devices to work correctly. Without operating reserve, even small problems could cause big blackouts.
See also
 In Spanish: Reserva operativa para niños
In Spanish: Reserva operativa para niños