Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration facts for kids
Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (say: pan-toh-THEN-ate KY-nase uh-SOH-shee-ay-ted NOOR-oh-dee-jen-uh-RAY-shun), often called PKAN for short, is a very rare brain condition. It's also known as Hallervorden-Spatz disease. This disease mainly affects how people move and remember things. It's a "degenerative" disease, which means it slowly gets worse over time. Scientists believe it happens because too much Iron builds up in certain parts of the brain.
What Are the Symptoms?
PKAN usually starts when people are young, often in childhood or teenage years. The symptoms can be very serious and make daily life challenging.
Some common symptoms include:
- Shaking or trembling in the arms and legs.
- Feeling weak in the muscles.
- Sudden, uncontrolled tightening of muscles, called spasms.
- Problems with balance and coordination.
- Difficulty speaking clearly.
- Memory problems or trouble thinking.
What Causes PKAN?
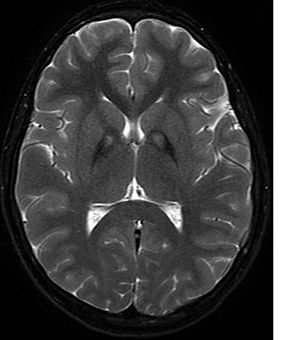
PKAN is a genetic disease. This means it's caused by a change, or "mutation," in a specific gene. The gene involved is called PANK2. This gene helps the body make an important protein called pantothenate kinase. When the PANK2 gene doesn't work right, it leads to problems with how the body uses iron. This can cause iron to build up in parts of the brain, especially in an area called the globus pallidus. This iron buildup damages brain cells and causes the symptoms of PKAN.
How Is PKAN Diagnosed?
Doctors might suspect PKAN if a person has the typical symptoms, especially if they start at a young age. To confirm the diagnosis, doctors often use special tests:
- MRI Scan: A type of brain scan called Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) can show the iron buildup in the brain. This often looks like a "tiger's eye" on the scan.
- Genetic Testing: This is the most accurate way to diagnose PKAN. Doctors can take a blood sample and check for changes in the PANK2 gene.
Is There a Cure?
Currently, there is no cure for PKAN. However, treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve a person's quality of life. These treatments might include:
- Medications: To help control muscle spasms, stiffness, or other movement problems.
- Physical Therapy: To help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
- Occupational Therapy: To help with daily tasks and activities.
- Speech Therapy: To help with speaking and swallowing difficulties.
Researchers are always working to learn more about PKAN and find new ways to treat it.
See also
 In Spanish: Neurodegeneración asociada a pantotenato quinasa para niños
In Spanish: Neurodegeneración asociada a pantotenato quinasa para niños