Pareto efficiency facts for kids
Multi-criteria optimization (also called multiobjective optimization) is a way to solve problems that have many different goals. Imagine you want to design a car that is both fast and fuel-efficient. These are two different goals. Multi-criteria optimization helps find the best possible solutions when you have several things you want to achieve at once.
One important idea from this field is Pareto efficiency. This concept was named after Vilfredo Pareto, an Italian economist. It describes a situation where you can't make one person or thing better off without making someone or something else worse off.
Contents
What is Pareto Efficiency?
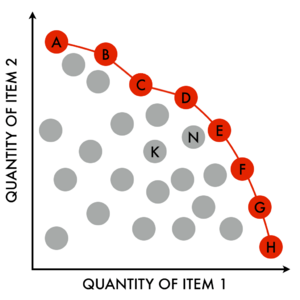
In simple terms, a situation is Pareto efficient if it's impossible to improve one person's situation without harming another person. Think of it like sharing a pizza. If the pizza is cut and everyone has a slice, and you can't give more pizza to one person without taking it from another, then that's a Pareto efficient way to share the pizza.
Pareto Efficiency in Economics
When we talk about an economy, Pareto efficiency means that all its resources are being used as well as they can be. These resources include things like machines, workers, land, and new ideas. If an economy is Pareto efficient, it's making the most of everything it has.
This state is often called being on the Pareto Frontier or Production Possibility Frontier. It means if the economy wants to make more of one product, it has to make less of another. This is because all its resources are already busy making things. There are no unused resources to make more of something new without taking them away from something else.
Is Pareto Efficiency Fair?
Just because something is Pareto efficient, it doesn't mean it's fair. For example, imagine one person owns everything in the world. This situation would be Pareto efficient because you couldn't make anyone else better off without taking something from that one person, which would make them worse off.
So, while Pareto efficiency means resources are used fully, it doesn't guarantee that wealth or benefits are shared equally among everyone. It only means that no one can improve without someone else losing out.
How Multi-Criteria Optimization Helps
Multi-criteria optimization helps people and businesses make smart choices when they have many goals. For example, a company might want to make a product that is:
- Low in cost
- High in quality
- Safe to use
- Good for the environment
It's hard to make a product that is perfect in all these areas at once. Multi-criteria optimization helps find the best balance. It shows the different "Pareto efficient" options. These are the options where you can't improve one goal (like lower cost) without making another goal worse (like lower quality).
By understanding these trade-offs, decision-makers can choose the solution that best fits their needs. They can see what they gain and what they might lose with each choice.
See also
- In Spanish: Eficiencia de Pareto para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |