Perfect competition facts for kids
In economics, perfect competition is a special kind of market where lots of companies sell the exact same product or service. No single company is big enough to set the price on its own without losing customers.
Because the rules for perfect competition are very strict, there are only a few markets that truly fit this description. This idea mostly helps us compare and understand other types of markets.
What Makes a Perfectly Competitive Market?
A perfectly competitive market exists when every business in it acts as a "price taker." This means they have to accept the market price. They cannot charge a different price without losing all their customers.
Here are the main things that make a market perfectly competitive:
- Lots of buyers and sellers: There are many people who want to buy the product at a certain price. And there are many businesses ready to sell it at that price.
- Easy to join or leave: New businesses can easily start selling in the market. Existing businesses can also leave without any problems. There are no big costs or rules stopping them.
- Everyone knows everything: Buyers know the price of the product from all sellers. Sellers also know how their competitors make their products. This means no secrets!
It's very hard for these conditions to be completely true in real life. For example, it always costs some money to start a new business. So, there are always some small barriers to entry. Also, people never know absolutely everything. Buyers can't know every single price, and businesses don't share all their production secrets.
However, studying perfect competition is still important. It helps us understand how other markets work by comparing them to this ideal model.
In the long run, businesses in a perfectly competitive market are very efficient. This means they use their resources in the best possible way. They produce goods at the lowest possible cost and offer them at a fair price.
How We Model Perfect Competition
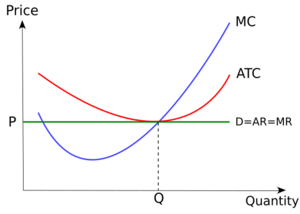
We can use a diagram to show how a perfectly competitive business decides its price and how much to produce. The picture shows the costs for a business in a perfectly competitive market when it's settled for a long time.
- The MC curve (in blue) shows the extra cost to make one more unit of a product.
- The ATC curve (in red) shows the average total cost to make each unit.
- The demand curve (in green) is a flat line. This is because there are so many buyers and sellers that one business cannot change the market price. This line also shows the average money earned per unit and the extra money earned from selling one more unit.
Businesses always try to make the most profit. So, a business will produce at the point where the extra cost of making one more unit (MC) equals the extra money it earns from selling that unit (MR). In the diagram, this happens at output level Q.
At this point, the average total cost curve also touches the demand curve. This means the business is earning "normal profits." This is just enough profit to keep the business running, but not extra large profits.
| Different Market forms |
|---|
| Perfect competition • Monopolistic competition • Oligopoly • Oligopsony • Monopoly • Natural monopoly • Monopsony |
See also
 In Spanish: Competencia perfecta para niños
In Spanish: Competencia perfecta para niños