Monopoly facts for kids
A monopoly (from the Greek words monos, meaning "one," and polein, meaning "to sell") is when there's only one main seller of a product or service in a specific market. Imagine if only one company made all the video games or sold all the internet service in your town. That company would have a lot of power because people can't easily buy from anyone else.
This usually happens when there's no real competition for that product or service, and there are no good substitutes. For example, if you need electricity, and only one company provides it, that's a monopoly.
In economics, a monopoly means a single producer. In law, it means a company with so much power that it can charge very high prices. It doesn't matter if the company is big or small, just how much power it has over the market.
A monopoly can be created in different ways. Sometimes, a government might allow one company to be the only seller. Other times, a few companies might join together to form one big one. Or, a monopoly can happen naturally, becoming a natural monopoly. For example, utilities like telephone service or cable television are often natural monopolies. It costs a lot of money to build all the wires and equipment for another company to compete. Because of this, governments often allow these natural monopolies but control them strictly. This stops them from charging unfair prices.
Many countries, including the United States, have laws to prevent companies from becoming monopolies or to limit what they can do if they are one. These laws aim to protect consumers and encourage fair competition.
Contents
What makes a monopoly special?
In classical economics, a monopoly has a few key features:
- They want to make the most money: Just like any other business, a monopoly tries to earn as much profit as possible. They figure out the best amount of product to sell to do this.
- They set the prices: Because they have a lot of power in the market, a monopoly can decide the prices for their products or services. They set prices based on how much people want their product.
- It's hard for others to join: There are big obstacles that stop other companies from entering the market. These obstacles can be natural, like the high cost of building a power grid, or artificial, like special laws or patents.
How monopolies affect the market
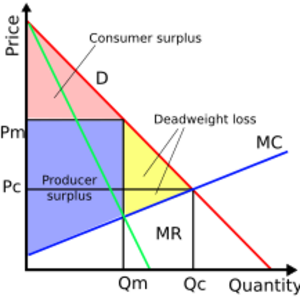
A monopoly wants to make the most money. Since there are no other big companies, the monopoly can set its own prices. They will set a price that gives them the most profit. However, this often means customers have to pay more for the same product.
When a monopoly sets its price to maximize profit, it usually produces less of the product than what would be best for everyone in society. If more of the product were made, it would benefit more people. The difference between what's produced and what's best for society is called a deadweight loss. This means a monopoly isn't as efficient as it could be for society as a whole.
Sometimes, monopolies can earn a lot of profit over a long time. This extra money can be used for new innovation or to make their production more efficient. However, some people worry that without competition, a monopoly might become lazy and not bother to innovate at all.
Natural monopolies
A natural monopoly can happen when it's just too expensive for more than one company to operate in a market. This is often because the cost of setting up the business (like building a huge network of pipes or wires) is very high. For example, it's cheaper for one company to provide water to a whole city than for two or three companies to build separate water systems.
A natural monopoly keeps getting cheaper to produce more as it grows. This means the average cost of making the product keeps going down across the entire market demand. So, it's most efficient and cheapest for just one company to provide the product or service.
Like other monopolies, natural monopolies can sometimes be inefficient if left unchecked. That's why governments often create laws to control them. These laws usually focus on making sure the natural monopoly sets fair and affordable prices for its services.
Related pages
| Different Market forms |
|---|
| Perfect competition • Monopolistic competition • Oligopoly • Oligopsony • Monopoly • Natural monopoly • Monopsony |
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Monopolio para niños
In Spanish: Monopolio para niños