Periodontitis facts for kids
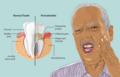
Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that affects the tissues around your teeth. It's more severe than Gingivitis, which is a milder gum inflammation. Periodontitis doesn't just affect your gums; it also damages the bone that holds your teeth in place. If it's not treated, it can lead to loss of teeth.
The name "periodontitis" helps us understand what it is. It comes from three Greek words: "peri" meaning around, "odont" meaning tooth, and "-itis" meaning inflammation or redness. So, it's an inflammation around the tooth.
Contents
What Causes Periodontitis?
Periodontitis usually starts when plaque builds up on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria. If plaque isn't brushed away, it can harden into something called tartar. Tartar is very hard to remove with just brushing.
How Bacteria Affect Gums
The bacteria in plaque and tartar irritate your gums. This irritation makes your gums red, swollen, and they might bleed easily. This first stage is called gingivitis. If gingivitis isn't treated, the inflammation can spread deeper.
When Gums Pull Away
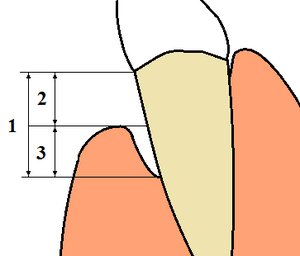
Over time, the inflammation can cause your gums to pull away from your teeth. This creates small pockets. These pockets then become filled with more plaque and tartar, along with bacteria. The bacteria in these pockets can damage the bone and tissues that support your teeth.
Signs You Might Have Periodontitis
It's important to know the signs of periodontitis so you can get help early.
- Bleeding Gums: Your gums might bleed when you brush or floss.
- Swollen or Red Gums: Gums that look puffy or bright red.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath that doesn't go away.
- Loose Teeth: Your teeth might start to feel wobbly.
- Changes in Bite: Your teeth might not fit together the same way when you bite.
- Receding Gums: Gums that pull away from your teeth, making them look longer.
How to Prevent Periodontitis
The good news is that periodontitis is often preventable!
Good Oral Hygiene Habits
- Brush Your Teeth: Brush at least twice a day for two minutes each time. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush.
- Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under the gum line.
- Use Mouthwash: An antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce bacteria.
Regular Dental Check-ups
- Visit Your Dentist: See your dentist for regular check-ups and professional cleanings. They can remove plaque and tartar that you can't reach.
- Early Detection: Dentists can spot early signs of gum disease and help you treat it before it gets worse.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Periodontitis para niños
In Spanish: Periodontitis para niños