Persian spider gecko facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Persian spider gecko |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Gekkonidae |
| Genus: | Agamura |
| Species: |
A. persica
|
| Binomial name | |
| Agamura persica Duméril, 1856
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
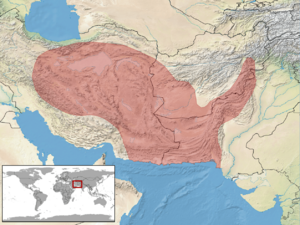
The Persian spider gecko (Agamura persica) is a unique reptile. It lives in dry, rocky areas called semideserts. You can find it in countries like Iran, Pakistan, and Afghanistan. These places have very hot summers and very cold winters.
This gecko gets its name because it looks a bit like a spider! It has long, thin legs and a slender tail. These features help it climb easily on rocks in its habitat (the place where it lives). Its toes are thin and have claws. They are also bent in a special way, which is why it's called an "angular-toed gecko."
Contents
What Makes the Persian Spider Gecko Special?
Size and Appearance
Female Persian spider geckos are usually between 42 and 77 millimeters long. Their tails can be 34 to 59 millimeters long. Males are a bit smaller, from 35 to 65 millimeters long, with tails from 27 to 59 millimeters.
This gecko has a light gray body on top. It often has some yellow color mixed in. It also has five dark stripes across its back. These stripes are almost as wide as the light spaces between them. Its tail has about 9 to 10 dark stripes, and its belly is a speckled gray color.
Different Types of Persian Spider Geckos
There are two main types, or subspecies, of the Persian spider gecko:
- Agamura persica ssp. persica: This type lives in the eastern parts of its range, like eastern Iran and Afghanistan. It has three dark stripes on its back. One is on its neck, one behind its shoulders, and one near its hips.
- Agamura persica ssp. cruralis: This type is found in the western parts, mostly in Iran. It has five darker brown stripes on its back. The first is on its neck, and the fifth is near its hips. It also has nine to ten stripes on its tail.
Life in the Wild
Where Do They Live?
Persian spider geckos prefer rocky and stony places. They live on hillsides and flat, dry lands near sandy semideserts.
Daily Habits and Adaptations
These geckos are mostly nocturnal, meaning they are active at night. However, you might see them during the day. They sometimes bask (lie in the sun) to warm up. They can be active even when the ground is very hot, up to 44°C (about 111°F)!
The Persian spider gecko has a special "eyelid" that doesn't move. It acts like a built-in "sunshade." This helps protect its eyes from the bright sun during the day.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Persian spider geckos are ready to have babies when they are about 18 to 24 months old. Their breeding season is from March to May. The females lay their eggs in June, and the baby geckos hatch and appear in September.
Telling Males and Females Apart
It's fairly easy to tell male and female Persian spider geckos apart.
Male Features
Male geckos have a noticeable bulge near the base of their tail. This is where their reproductive organs are. Because the gecko is so thin, this bulge is quite easy to see from the side. Males also have two to four special pores (tiny holes) in front of their back legs. These are called preanal pores.
Female Features
Female geckos do not have this bulge or the preanal pores.
Young Geckos
Young male geckos don't have the bulge when they are very young. It usually starts to show when they are about 8 to 12 weeks old, or when they are about 7–8 centimeters long. Sometimes, it might take a bit longer, up to four to six months.
Images for kids