Physical cosmology facts for kids
Physical cosmology is a part of astronomy and physics. It studies the universe as a whole. Scientists in this field try to understand how the universe began, how it has changed over time, and what its future might be. They use ideas from physics and astronomy to explain the biggest structures in space, like galaxys and galaxy clusters.
Contents
What is Physical Cosmology?
Physical cosmology is like solving a giant puzzle about the universe. It asks big questions such as:
- How did the universe start?
- What is it made of?
- How big is it?
- What will happen to it in the future?
To answer these questions, scientists use powerful telescopes and complex math. They look for clues in the light from distant stars and galaxies. They also study tiny particles and forces here on Earth.
The Universe's Beginning: The Big Bang
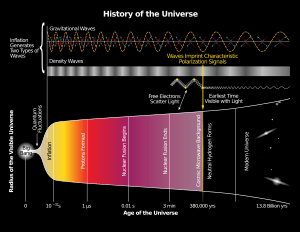
One of the most important ideas in physical cosmology is the Big Bang theory. This theory says that the universe started from a very hot, dense point about 13.8 billion years ago. From this tiny point, the universe rapidly expanded and cooled.
Evidence for the Big Bang
Scientists have found several pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory:
- Expanding Universe: Almost all galaxies are moving away from us, and the farther away they are, the faster they move. This shows the universe is still expanding, like a balloon being blown up.
- Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): This is a faint glow of radiation that fills the entire universe. It's like an echo or leftover heat from the very early universe, right after the Big Bang.
- Abundance of Light Elements: The amounts of light elements like hydrogen and helium in the universe match what the Big Bang theory predicts. These elements were formed in the first few minutes after the Big Bang.
What is the Universe Made Of?
When we look at the universe, we see stars, planets, and galaxies. But scientists believe that most of the universe is made of things we cannot see or touch directly.
Dark Matter
Dark matter is a mysterious substance that doesn't give off, reflect, or absorb light. We can't see it, but we know it's there because of its gravity. Dark matter helps hold galaxies together. Without it, galaxies would spin apart. Scientists think dark matter makes up about 27% of the universe.
Dark Energy
Dark energy is an even more mysterious force. It is thought to be responsible for the universe's accelerating expansion. Instead of slowing down, the universe is expanding faster and faster. Dark energy is believed to make up about 68% of the universe.
Ordinary Matter
All the stars, planets, and everything we can see and touch is called ordinary matter. This includes you, me, and everything on Earth. Ordinary matter makes up only about 5% of the universe.
The Future of the Universe
Cosmologists also try to predict what will happen to the universe in the far future. Because of dark energy, the universe is expanding faster. This could lead to a few possible outcomes:
- Big Freeze (Heat Death): The universe keeps expanding, getting colder and colder. Stars will eventually run out of fuel, and everything will become dark and frozen.
- Big Rip: If dark energy gets stronger, it could eventually tear apart galaxies, stars, planets, and even atoms.
- Big Crunch: (Less likely with current evidence) If gravity were stronger than dark energy, the expansion could stop and reverse, causing the universe to collapse back into a hot, dense state.
Most scientists currently believe the Big Freeze is the most likely future for our universe.
Why is Physical Cosmology Important?
Studying physical cosmology helps us understand our place in the vast universe. It pushes the boundaries of human knowledge and helps us develop new technologies. For example, the study of the Big Bang led to the development of better radio telescopes and detectors. It also helps us appreciate the incredible scale and complexity of the cosmos.
See also
 In Spanish: Cosmología física para niños
In Spanish: Cosmología física para niños