Proxy server facts for kids
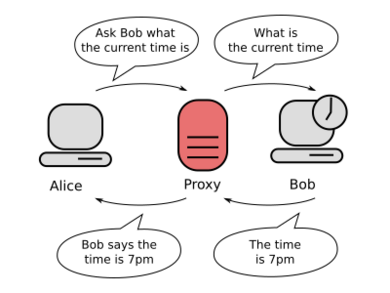
Imagine you want to ask a friend a question, but you don't want them to know it's you asking. So, you ask another friend to ask for you. That's kind of how a proxy server works!
In computer terms, a proxy server is like a middleman between your computer (the client) and another computer (the server) that has the information you want, like a website. Instead of your computer talking directly to the website's server, it sends its request to the proxy server first. The proxy server then gets the information for you and sends it back.
This "middleman" can help in many ways. It can make your internet use more private, keep you safer online, or even make websites load faster. Proxies were created to help organize and protect how different computers talk to each other on the internet.
Contents
What Are the Different Kinds of Proxies?
A proxy server can be on your own computer, or it can be somewhere else between your computer and the websites you visit.
- A proxy that just passes requests without changing them is often called a gateway.
- A forward proxy is used to get information from many different places on the internet. It sits between you and the internet.
- A reverse proxy usually sits in front of a server on a private network. It helps control and protect who can access that server. Reverse proxies also help share the work among many servers and keep things secure.
Open Proxies: Proxies for Everyone
An open proxy is a type of proxy server that anyone on the internet can use. In 2008, an expert named Gordon Lyon said there were "hundreds of thousands" of open proxies online.
- Anonymous proxy: This type of proxy tells the website that it's a proxy, but it hides your computer's real internet address (IP address). This can be helpful if you want to keep your location private.
- Transparent proxy: This proxy also tells the website it's a proxy, and it might even share your computer's original IP address. The main reason people use these is to make websites load faster by saving copies of them.
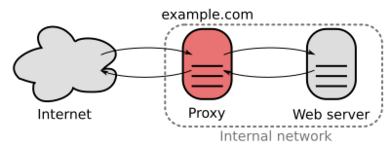
Reverse Proxies: Protecting Servers
A reverse proxy acts like a regular server to people visiting a website. But behind the scenes, it sends their requests to one or more other servers that actually handle the work. The website visitor doesn't even know there are other servers involved. Reverse proxies are usually placed near web servers and handle all the internet traffic coming to those servers.
Here are some reasons why reverse proxies are used:
- Making websites secure: They can handle the special coding (encryption) needed for secure websites, like those that start with "https://".
- Sharing the work: They can send requests to different web servers, so no single server gets overloaded. This is called load balancing.
- Serving fast content: They can store copies of things like pictures or videos, so the main web servers don't have to send them every time.
- Making things smaller: They can compress information to make websites load faster.
- Security: They add an extra layer of protection against attacks on web servers.
- Access from outside: They can help people outside a company's network safely access certain internal services.
Forward Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy: What's the Difference?
A forward proxy helps protect the people using a network. It sits between your computer and the internet, controlling what you can access and hiding your computer's identity. It makes your internet use safer and helps follow rules set by your network.
A reverse proxy, on the other hand, protects the servers that host websites. It takes requests from visitors, sends them to one of many servers, and then sends the answer back to the visitor. It acts like a shield for the servers, hiding their real identity.
How Are Proxies Used?
Proxies have many different uses, from keeping you safe to making the internet faster.
Watching and Filtering What You See
Controlling Content
A proxy server can help control what information goes in and out of a network. Schools and businesses often use these to make sure internet use follows their rules.
These proxies can:
- Ask users to log in to access the internet.
- Keep records of which websites people visit.
- Scan incoming information for viruses and other harmful software.
Many schools and workplaces block certain websites. They do this using special proxies called content filters. These filters can block websites based on their address, keywords, or even the type of content they have. For example, they might block sites related to games or social media.
Some students try to get around these filters by using other proxy websites. However, this can sometimes be risky because you might be sending your information through an unknown server.
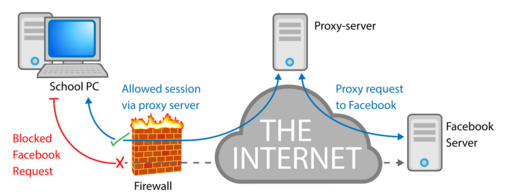
Bypassing Filters and Censorship
If a website only allows people from certain countries to access it, you can use a proxy server located in that country to get around the restriction. This is a common way people get around government censorship in some parts of the world.
Keeping Records and Listening In
Proxy servers can be set up to watch all the information flowing between your computer and the internet. This means that anything you send or receive, including passwords or cookies, could be seen by the person running the proxy. That's why it's super important to always use secure connections (like those starting with "https://") for things like online banking or email.
Using a chain of proxies can make it harder to trace your online activity. However, each proxy in the chain leaves a trace, and if you don't know who runs those proxies, you might not be as safe as you think. Sometimes, using a proxy can also lead to you being blocked from certain websites if the proxy's address has been used for spam or other bad behavior.
Making Things Faster
A caching proxy server saves copies of websites and files that people have asked for before. If someone asks for the same thing again, the proxy can give them the saved copy, which is much faster than getting it from the original server. This helps large organizations save internet bandwidth and makes websites load quicker. Many internet providers and big businesses use caching proxies.
There are also special proxies called Performance Enhancing Proxies (PEPs). These are used to make internet connections work better, especially over wireless networks or when there's a lot of delay. They can help speed up how data is sent and received.
Translating Websites
A translation proxy helps make websites available in different languages. When you visit a website through a translation proxy, the proxy sends your request to the original website. As the information comes back, the proxy translates the content into your language before sending it to your browser. This can be done using computer translation or human translation.
Accessing Services Anonymously
An anonymous proxy server tries to hide who you are when you browse the internet. The website you visit sees the request coming from the proxy, not from your computer. However, the proxy server itself knows who you are, so you need to trust the people running it. Many anonymous proxies are supported by showing ads to users.
Some anonymous proxies might still send information that could reveal your computer's address. The best ones, called "elite" or "high-anonymity" proxies, make it seem like the proxy server is the one visiting the website. To be extra safe, you might want to clear your cookies and browser cache when using these.
Checking Ads Based on Location
Advertisers use proxy servers to check if their ads are showing up correctly in different locations. By using a proxy in a specific country or city, they can see how their ads appear to people in that area.
Security
A proxy can help keep a company's internal network structure a secret, which adds to its computer security. It makes requests from computers inside the network appear anonymous. Proxies can also work with firewalls to create a stronger defense.
However, if a proxy is set up incorrectly, it could accidentally open up a network that was supposed to be private to the internet.
Sharing Resources Across Different Websites
Proxies allow websites to get information from other websites (like images or music files) even when normal rules would prevent them from doing so directly. This helps websites use content hosted elsewhere while still keeping things secure.
Bad Uses of Proxies
Buying Limited Products
Sometimes, people who buy and resell limited products (like special sneakers or concert tickets) use web proxy servers. They do this to get around limits on how many items one person can buy online.
How Proxies Are Built
Web Proxy Servers
Web proxies handle requests for web pages (HTTP requests). When your browser sends a request to a web proxy, it includes the full website address. The proxy then gets the page and sends it back to you.
Some web proxies can also set up a secure "tunnel" for other types of traffic, like secure HTTPS connections.
Examples of web proxy software include Apache, HAProxy, Nginx, Squid, and Varnish.
SOCKS Proxy
SOCKS is another type of proxy that can forward different kinds of data, similar to how web proxies handle secure connections.
Transparent Proxy
A transparent proxy (also called an intercepting proxy) works without you even knowing it's there. It intercepts your internet traffic without needing any special setup on your computer. These proxies are usually placed between your computer and the internet, acting like a part of your network's gateway or router.
Transparent proxies are often used in businesses to make sure everyone follows internet rules and to make it easier for network administrators, since they don't have to set up each computer individually. Internet providers in some countries also use them to save bandwidth and make things faster for customers by caching content.
Problems with Transparent Proxies
Because transparent proxies intercept your connection, they can sometimes cause issues. For example, they might make it harder for websites to know your original destination, or they could interfere with how some secure connections work.
How to Spot a Transparent Proxy
There are a few ways to tell if you're using a transparent proxy:
- You can compare your computer's external IP address (what the internet sees) with what an external website sees.
- You can check if secure (HTTPS) websites behave differently than regular (HTTP) ones, as many transparent proxies don't intercept secure connections.
- You can use tools that show the path your internet traffic takes.
CGI Proxy
A CGI web proxy lets you access websites by typing the website address into a special form on a web page. This is useful if your device or network doesn't let you change its regular proxy settings. The first known CGI proxy was created in 1996 by James Marshall.
Many CGI proxies use software like CGIProxy, Glype, or PHProxy. While they are less popular now due to other privacy tools like VPNs, hundreds of them are still online. Some CGI proxies were made to help people with disabilities access websites, but many had to shut down because too many people used them to get around filters.
Suffix Proxy
A suffix proxy lets you access web content by adding the proxy server's name to the end of the website's address (e.g., "en.wikipedia.org.SuffixProxy.com"). These are easy to use but don't offer much privacy and are mainly for bypassing simple web filters. However, modern filters can often detect them.
Tor Onion Proxy Software
Tor is a system designed to help people stay anonymous online. The Tor software sends your internet traffic through a worldwide network of volunteer servers. This makes it very hard for anyone to figure out your computer's location or what you're doing online. Using Tor helps protect your privacy and freedom on the internet.
Tor uses something called "onion routing." This means your data is encrypted (scrambled) multiple times, like layers of an onion. Each Tor server in the network peels off one layer of encryption before passing the data to the next server. This makes it very difficult for anyone to understand your original data as it travels.
I2P Anonymous Proxy
The I2P anonymous network is another proxy network focused on online anonymity. It uses a method called "garlic routing," which is an improved version of Tor's onion routing. I2P is spread out across many computers and works by encrypting all communications in several layers. These encrypted messages are then sent through a network of volunteer-run computers in different places. By hiding where the information comes from, I2P helps prevent censorship. I2P aims to protect users' freedom, privacy, and ability to do private business online.
Every I2P user runs an I2P "router" on their computer. This router finds other I2P users and builds anonymous tunnels through them. I2P can provide proxies for many different internet protocols, like HTTP (for web pages) and IRC (for chat).
Proxies vs. Network Address Translators (NAT)
A proxy works at a higher level of internet communication, like an application. Network address translation (NAT) is similar but works at a lower level, dealing with network addresses.
NAT is simpler and uses fewer computer resources than a proxy. However, a proxy is more flexible. A "transparent firewall" combines the benefits of a proxy without the user knowing it's there. It sends network traffic to the proxy for closer inspection.
DNS Proxy
A DNS proxy server takes requests for website names (like "google.com") from your local network and sends them to a larger internet server that knows the actual computer address for that name. It can also save copies of these name-to-address translations to speed things up.
Proxifiers
Some computer programs can "SOCKS-ify" requests. This means they can adapt other software to connect to the internet through certain types of proxy servers, especially SOCKS proxies.
Residential Proxy
A residential proxy uses a real internet address provided by an internet service provider (ISP), like the one your home computer or phone uses. When you use a residential proxy, your requests go through these real home IP addresses. This makes it look like your internet traffic is coming from a regular person's device, making it harder for websites to identify you as a proxy user.
Some residential proxies are part of networks where people volunteer their devices. However, some residential proxies might be running on computers that have been secretly taken over by harmful software. Researchers have found that some of these proxies have been used for bad activities like illegal promotions or spreading malware.
See also
 In Spanish: Servidor proxy para niños
In Spanish: Servidor proxy para niños
- Application firewall
- Captive portal
- Darknet
- Internet privacy
- Virtual private network
- Web cache