Mohr oak facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Mohr oak |
|
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Quercus
|
| Species: |
mohriana
|
 |
|
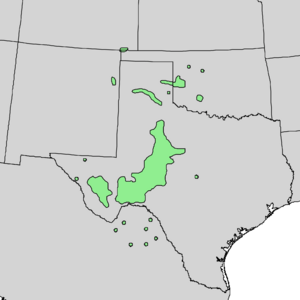
| Natural range | |
The Mohr oak (also called shin oak or scrub oak) is a special kind of evergreen plant. This means it keeps its leaves all year round! It can be a small tree or a bush. You can find it growing in the southern United States and northern Mexico.
It belongs to the group of plants known as white oaks. The scientific name, Quercus mohriana, was given to honor a botanist named Charles Mohr. He was a pharmacist and plant expert from Alabama.
Contents
Where the Mohr Oak Lives
The Mohr oak grows mostly in western Texas. It is very common there. You can also find it in other states like Oklahoma and New Mexico. It even grows south of the border in Coahuila, Mexico.
What the Mohr Oak Looks Like
The Mohr oak can grow up to 6 meters (20 feet) tall. Sometimes it grows as a small tree. Other times, it forms a large, thick bush. Its bark is light brown and feels rough. It has deep grooves in it.
Leaves and Branches
The young branches are yellowish or whitish. They feel soft because they are covered in tiny hairs. As they get older, these branches become smooth. The buds are a dark red-brown color. They have a few hairs on them.
The leaves are shiny and feel like leather. They are a dark blue-gray color on top. Underneath, they are covered in light gray hairs. The edges of the leaves are usually smooth. Sometimes, they might have a few small teeth.
Flowers and Acorns
In the spring, the Mohr oak grows reddish flowers. It has two types of flowers. The female flowers grow in small groups of one to three. The male flowers grow in longer clusters with many flowers.
The acorns are light brown and shaped like a wide egg. They have a rounded top. The acorns grow alone or in pairs. Their cups are quite deep.
Where the Mohr Oak Likes to Grow
The Mohr oak prefers dry places. It often grows on hillsides made of limestone. These areas are usually between 600 and 2500 meters (2000–8300 feet) above sea level.
It likes to live in areas called chaparral and desert scrub savanna. Chaparral is a type of shrubland. Savanna is a grassland with scattered trees. This oak does well in places that get less than 63 centimeters (25 inches) of rain each year.
Plant Neighbors
The Mohr oak often grows near other interesting plants. Some of its neighbors include:
- True mountain-mahogany (Cercocarpus montanus)
- Desert ceanothus (Ceanothus greggii)
- Sandpaper oak (Quercus pungens)
- Oneseed juniper (Juniperus monosperma)
- Cane cholla (Opuntia imbricata)
- Purplefruited pricklypear (Opuntia phaeacantha)
- Mexican buckeye (Ungnadia speciosa)
- Texas persimmon (Diospyros texana)
- Hairy tridens (Erioneuron pilosum)
- Plateau oak (Quercus fusiformis)
See also
 In Spanish: Quercus mohriana para niños
In Spanish: Quercus mohriana para niños


