Radiation Exposure Compensation Act facts for kids
 |
|
| Long title | An Act to provide jurisdiction and procedures for claims for compassionate payments for injuries due to exposure to radiation from nuclear testing. |
|---|---|
| Acronyms (colloquial) | RECA |
| Nicknames | Radiation Exposure Compensation Act of 1990 |
| Enacted by | the 101st United States Congress |
| Effective | October 15, 1990 |
| Citations | |
| Public law | 101-426 |
| Statutes at Large | 104 Stat. 920 |
| Codification | |
| Titles amended | 42 U.S.C.: Public Health and Social Welfare |
| U.S.C. sections amended | 42 U.S.C. ch. 23 § 2210 et seq. |
| Legislative history | |
|
|
The United States Radiation Exposure Compensation Act (RECA) is a special law. It helps people who got sick because of radiation. This radiation came from two main sources. One was nuclear testing done by the U.S. during the Cold War. The other was working with uranium (mining, milling, or moving it).
This law gives money to people who were harmed. It helps them with their medical costs and other needs. It's a way for the government to apologize and help those affected.
Contents
What is the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act?
The RECA law provides money to people who developed certain illnesses. These illnesses must be a direct result of radiation exposure. The law covers different groups of people.
Here are the main groups and the amounts they can receive:
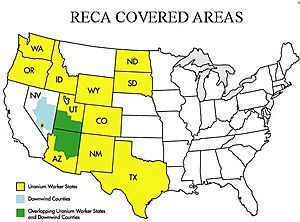
- $50,000 for people living or working "downwind" of the Nevada Test Site. These people were affected by nuclear fallout.
- $75,000 for workers who took part in atmospheric nuclear weapons tests.
- $100,000 for uranium miners, millers, and people who moved uranium ore.
To get this money, people need to meet other requirements. They must prove their exposure and show they have specific medical conditions. They also need to show how long they worked in certain jobs.
Why Was This Law Created?
People started trying to create this law in the late 1970s. Senator Ted Kennedy was one of the first to propose a bill in 1979. This early bill wanted to help people exposed to nuclear fallout. It also aimed to help uranium miners or their families.
The bill focused on miners who worked in Utah, Colorado, New Mexico, and Arizona. It covered the years between 1947 and 1961. It also listed specific illnesses like leukemia and thyroid cancer.
The first ideas for the law included areas in Utah and Nevada. It even wanted to help ranchers whose sheep died after nuclear tests. It took 12 years for a similar bill to finally become law.
When the law passed, it added uranium miners from Wyoming. It also extended the time miners could have worked, up to 1971. The law included an apology from Congress. It said the nation was sorry to those who were "involuntarily subjected to increased risk of injury and disease." This was done to serve the country's security.
How Does the Act Work?
The Radiation Exposure Compensation Act became law on October 15, 1990. President George H. W. Bush signed it. At first, it was hard for some people to get their compensation. This was especially true for the families of uranium miners.
Many uranium miners were Native American. They often did not have standard marriage licenses. This made it hard to prove their connection to the deceased miner. In 1999, new rules were made to help these families.
Getting Help with Claims
Even with new rules, many workers and their families found the paperwork difficult. The rules for who qualified were also very strict. Because of this, many claims were turned down.
In 2000, more changes were made to the law. These changes added two new groups of people who could get money. These were uranium mill workers and ore transporters. They could receive the same amount as uranium miners. The changes also added more areas for "downwinders." They also recognized more illnesses and lowered the required radiation exposure for miners.
Further changes in 2002 fixed small errors in the law. They also made some points clearer. This helped ensure that more people could get the help they needed.
Who Can Get Compensation?
To get compensation, uranium industry workers must have certain health problems. These include lung cancer, lung fibrosis, or silicosis. For uranium mill workers and ore transporters, kidney cancer and chronic kidney disease are also covered. These conditions must be linked to their work.
How Many People Have Been Helped?
The RECA program has helped many people over the years.
- By July 2012, over 25,800 claims were approved. More than $1.7 billion was paid out.
- By March 2015, over $2 billion had been paid to 32,000 people.
- By April 2018, a total of 34,372 claims were approved. The total compensation paid was over $2.2 billion.
This shows that the law has provided significant help to many people affected by radiation.
See also
 In Spanish: Ley de compensaciones por exposición a la radiación para niños
In Spanish: Ley de compensaciones por exposición a la radiación para niños