Radioisotope heater unit facts for kids
A radioisotope heater unit (often called an RHU) is a special device that makes heat. It gets this heat from tiny pieces of material that are naturally breaking down. Think of it like a small, safe, and long-lasting heater that doesn't need electricity!
Contents
How Do These Heaters Work?
A radioisotope heater unit works using something called radioactive decay. This is a natural process where certain types of atoms are unstable. They slowly change into more stable atoms. When they change, they release energy.
The Power of Radioactive Decay
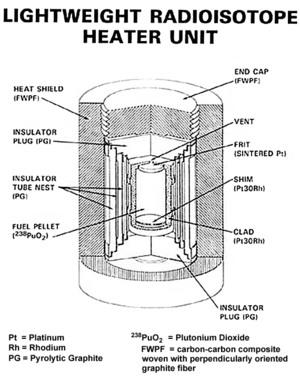
Inside an RHU, there's a small amount of radioactive material. This material is carefully placed inside a strong container. As the material breaks down, it releases energy. Most of this energy turns into heat. This heat keeps the RHU warm for a very long time. It's a bit like a tiny, never-ending warm pack.
Why They Are So Useful
RHUs are very special because they can make heat for many years without needing any power from batteries or solar panels. They are also very small and light. These features make them perfect for places where it's super cold and there's no way to plug things in.
Where Are RHUs Used?
Radioisotope heater units are mostly used in space. Space is an incredibly cold place, especially far away from the Sun. Spacecraft and their instruments need to stay warm to work correctly.
Keeping Spacecraft Warm
When a spacecraft travels far from Earth, like to the outer planets or beyond, the sunlight is too weak to keep it warm. This is where RHUs come in handy. They provide a constant, reliable source of heat. This heat protects sensitive electronics and scientific instruments from freezing.
For example, RHUs have been used on many NASA missions. They helped keep rovers and landers warm on Mars. They also kept instruments working on probes that explored the outer solar system, like the Voyager spacecraft. These probes have been traveling for decades, and their RHUs are still providing heat!
Protecting Instruments
Some scientific instruments need to be kept at a certain temperature to work properly. If they get too cold, they might stop working or even break. RHUs ensure these instruments stay warm enough to collect important data. This data helps scientists learn more about other planets and the universe.
Safety of RHUs
The radioactive material inside an RHU is very carefully contained. The units are designed to be extremely strong and safe. They are built to survive harsh conditions, like a rocket launch or even a crash landing. This keeps the radioactive material safely inside.
Scientists and engineers work hard to make sure RHUs are safe for both people and the environment. They use materials that are not very dangerous and seal them tightly. This way, the heat can get out, but the radioactive material stays locked inside.
See also
 In Spanish: Unidad de calor de radioisótopos para niños
In Spanish: Unidad de calor de radioisótopos para niños