Range (biology) facts for kids
In biology, the range or distribution of a species is the geographical area or habitat where that species lives naturally. Think of it as the map showing where you can find a certain type of animal or plant.
Sometimes, a species might live in different places during different times of the year. For example, many animals migrate. So, you might hear about their summer range (where they live in summer) and their winter range (where they live in winter). When we talk about animals, we often mean their natural range, which is the area they would live in without human interference.
Contents
How Species Spread Out
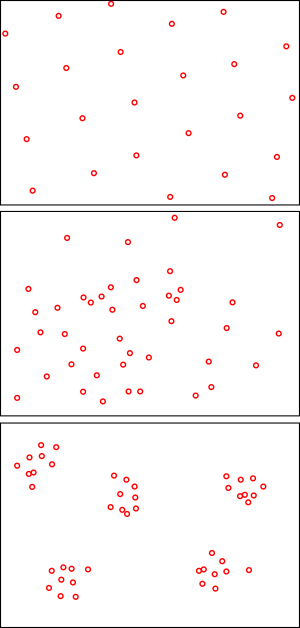
Species don't just spread out randomly across their range. They often follow certain patterns. Scientists have identified a few main types of distribution patterns:
Random Distribution
In a random distribution, individuals of a species are spread out unpredictably. Imagine throwing seeds on the ground; they land wherever they may. This pattern is not very common in nature because most species need specific conditions or resources.
Clumped or Grouped Distribution
This is the most common type of distribution. Individuals are found in groups or clusters. Think of a herd of elephants or a school of fish. This happens when resources like food or water are found in specific spots, or when living in groups offers protection or makes it easier to find mates.
Linear Distribution
A linear distribution means individuals are arranged in a line. This can happen if a species lives along a specific feature in the landscape, like a riverbank, a coastline, or a mountain ridge. For example, some plants might grow only along a certain type of soil line.
Radial Distribution
In a radial distribution, individuals spread out from a central point, like spokes on a wheel. This pattern is less common but can be seen in some plant species that spread their seeds outwards from a parent plant, or in animals that forage outwards from a central den or nest.
Regular or Ordered Distribution
A regular or ordered distribution means individuals are spaced out evenly. Imagine trees planted in neat rows in an orchard. In nature, this can happen when there is strong competition for resources, and individuals need a certain amount of space from their neighbors. For example, some desert plants release chemicals to prevent other plants from growing too close.
Images for kids
-
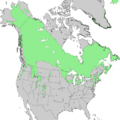
A species range map represents the region where individuals of a species can be found. This is a range map of Juniperus communis, the common juniper.
See also
 In Spanish: Área de distribución biogeográfica para niños
In Spanish: Área de distribución biogeográfica para niños