Reverberation facts for kids
Reverberation happens when sound waves keep bouncing around in a space even after the original sound has stopped. It's like a sound lingering or stretching out, making a room sound full. This is different from an echo, which is a single, clear repeat of a sound. Reverberation is many echoes happening very quickly, blending together.
Contents
What is Reverberation?
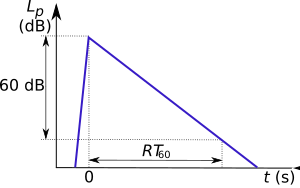
Reverberation is the way sound energy stays in a room. When you make a sound, like clapping your hands, the sound waves travel out. When they hit surfaces like walls, ceilings, and furniture, they bounce off. These bouncing sound waves continue to move around the room, slowly losing energy until they fade away completely.
How Does it Happen?
- Sound Waves Bounce: Sound travels in waves. When these waves hit a hard surface, they reflect, or bounce back.
- Many Reflections: In a room, sound waves hit many surfaces over and over again. Each time they bounce, they add to the lingering sound.
- Fading Away: With each bounce, the sound waves lose a little bit of energy. Eventually, they become too weak to hear. The time it takes for the sound to fade away is called the "reverberation time."
Where Do We Hear It?
We hear reverberation all the time, but it's more noticeable in some places:
- Large Rooms: Big spaces like concert halls, churches, or empty gymnasiums often have a lot of reverberation. This is because the sound waves have a long way to travel before hitting a surface, and there are many surfaces for them to bounce off.
- Hard Surfaces: Rooms with hard, smooth surfaces (like concrete, glass, or tile) will have more reverberation. These materials reflect sound very well.
- Soft Surfaces: Rooms with soft materials (like carpets, curtains, and upholstered furniture) will have less reverberation. These materials absorb sound, stopping it from bouncing around as much. This is why recording studios often have padded walls.
Why is Reverberation Important?
Reverberation can be good or bad, depending on the situation:
- Music: In concert halls, a certain amount of reverberation can make music sound richer and fuller. It helps blend the sounds of instruments together.
- Speech: Too much reverberation can make it hard to understand what someone is saying. The words can blur together, especially in large, echoey rooms. This is why classrooms and lecture halls are designed to reduce reverberation.
- Sound Design: Sound engineers use reverberation effects in movies, video games, and music to make sounds feel more realistic or to create a certain mood. For example, adding reverberation can make a voice sound like it's in a large cave.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Reverberación para niños
In Spanish: Reverberación para niños