Malabar gliding frog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Malabar gliding frog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Rhacophorus
|
| Species: |
malabaricus
|
 |
|
The Malabar gliding frog or Malabar flying frog (Rhacophorus malabaricus) is a special type of tree frog. You can find it in the Western Ghats mountain range in India. These frogs are famous for their amazing ability to "glide" through the air!
Contents
What Makes This Frog Glide?
The name "gliding frog" comes from how it moves. When it jumps from high up in the trees, it stretches out the skin between its toes. This skin acts like a parachute! It helps the frog slow down its fall.
These frogs can make incredible gliding jumps. They can leap as far as 9 to 12 meters (about 30 to 40 feet). That's like jumping across a small classroom! It's about 115 times their own body length.
Appearance of the Malabar Gliding Frog
This frog can grow to about 10 centimeters (4 inches) long. This makes it one of the bigger moss frogs. Female frogs are usually larger than the males.
Their back skin feels a bit bumpy. It is a bright, vivid green color with no other marks. This helps tell it apart from a similar frog, R. pseudomalabaricus. That frog has a black pattern on its back.
The frog's belly is pale yellow and feels rougher. It has extra skin flaps between its long legs. There's also a small triangle of skin at its heel. The skin between its fingers and toes is very wide and bright orange-red. This wide webbing is what helps it glide!
Where Do These Frogs Live?
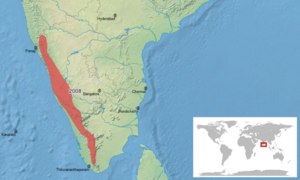
The Malabar gliding frog lives in the Western Ghats of India. They have been seen in the states of Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Karnataka, Goa, and Maharashtra. You can find them at different heights, from lowlands to high mountains.
They live in many places, like thick forests, younger forests, and even in farms or city areas. You can often spot them on leaves of trees near rivers or streams. During the time they lay eggs, they move to trees that hang over water. This is so their baby tadpoles can drop right into the water when they hatch.
Reproduction and Life Cycle
Reproduction for these frogs usually happens during the monsoon season. This is from June to September. Male frogs sit by stream banks and make calls to attract females. Females will then come closer to a male they want to mate with.
The males create a foamy nest. The females then lay their eggs in this foam. Sometimes, other male frogs will even help build these nests! After the eggs are laid, the male usually leaves. The female then covers the eggs with leaves.
These foam nests are usually about 7.8 to 11.2 centimeters long and 6.8 to 7.9 centimeters wide. A single nest can hold between 89 and 206 eggs! The eggs are off-white and don't have any color. When the eggs hatch, the tadpoles fall out of the foam nest and into the water below.
See also









