SN 1604 facts for kids
SN 1604 was a very bright supernova that people saw in the year 1604. A supernova is a huge explosion that happens when a star dies. This particular supernova appeared in the sky within the constellation called Ophiuchus.
SN 1604 is often called Kepler's Nova or Kepler's Supernova. It's named after Johannes Kepler, a famous astronomer who studied it closely. This event was very special because it was the last supernova seen in our own galaxy, the Milky Way, with the naked eye.
Contents
What is a Supernova?
A supernova is one of the biggest explosions in space. It happens when a star reaches the end of its life. There are two main ways a star can become a supernova.
How Massive Stars Explode
Very large stars, much bigger than our Sun, burn through their fuel quickly. When they run out of fuel, their core collapses very fast. This collapse creates a huge shockwave that blasts the star's outer layers into space. This explosion is incredibly bright.
White Dwarf Supernovae
Another type of supernova happens with a white dwarf star. A white dwarf is what's left after a smaller star dies. If a white dwarf is part of a binary system (two stars orbiting each other), it can pull material from its companion star. When it gathers too much material, it can explode.
Kepler's Supernova: A Historic Event
SN 1604 was a very important event for astronomers. It was so bright that people could see it even during the day for a while. It stayed visible for about 18 months.
Who Saw It?
Many people around the world saw this new "star." It was first noticed in early October 1604. The famous German astronomer Johannes Kepler began studying it on October 17, 1604. He wrote a book about his observations.
Why Was It Important?
Kepler's Supernova helped scientists learn more about stars. Before this, many people thought the heavens were perfect and unchanging. But a new, bright star appearing showed that changes could happen in space. This helped lead to new ideas in astronomy.
Where is SN 1604 Now?
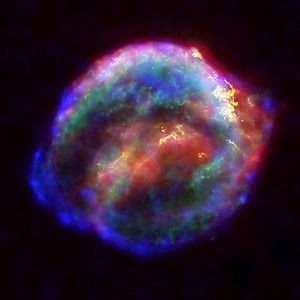
Today, we can't see the bright explosion of SN 1604 anymore. What's left is a cloud of gas and dust called a supernova remnant. This remnant is still expanding into space.
Studying the Remnant
Scientists use powerful telescopes to study the remnant of SN 1604. They look at it with X-ray, optical, and infrared telescopes. This helps them understand how stars explode and what happens to the material afterwards. The remnant is still very hot and glows in different types of light.
Last in Our Galaxy
SN 1604 is special because it's the last supernova we know of that exploded in our own Milky Way galaxy and was seen by people. Since then, we've seen supernovae in other galaxies, but none in ours. This makes SN 1604 a unique part of our galaxy's history.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: SN 1604 para niños
In Spanish: SN 1604 para niños
 | William M. Jackson |
 | Juan E. Gilbert |
 | Neil deGrasse Tyson |