Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm facts for kids
The Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm, also known as the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate, was a powerful Turkish kingdom in a region called Anatolia. Today, Anatolia is mostly the country of Turkey. This kingdom lasted for over 200 years, from 1077 to 1308.
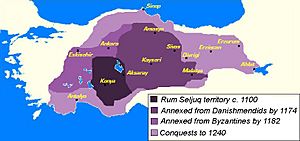
The Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm was formed after a big battle. In 1071, a group called the Seljuks won the Battle of Manzikert against the Byzantine Empire. This victory allowed the Seljuks to take control of Anatolia. By 1077, they had set up their own kingdom there, which they called the Sultanate of Rûm. The word "Rûm" came from the old Roman Empire, as the Seljuks saw themselves as heirs to that land.
Over time, the larger Seljuk Empire declined. Because of this, people started calling the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate simply the "Seljuk Sultanate." This kingdom eventually collapsed in 1308, partly due to invasions from the Mongols. After its fall, many smaller Turkish states, called Beyliks, were formed across Anatolia.
Contents
The Rise of the Sultanate
The Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm began its journey after the important Battle of Manzikert in 1071. In this battle, the Seljuk Turks defeated the Byzantine Empire. This win opened the door for the Seljuks to move into Anatolia.
By 1077, the Seljuks had established their own independent kingdom in Anatolia. This new kingdom was separate from the main Seljuk Empire. It quickly grew and became a major power in the region.
Life in the Sultanate
The Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm was known for its rich culture and impressive buildings. The rulers, called Sultans, encouraged art, science, and education. They built many beautiful mosques, schools (called madrasas), and places for travelers to rest (called caravanserais).
These buildings often had unique Seljuk designs, including detailed stone carvings and colorful tiles. Cities like Konya became important centers for learning and trade during this time. The Sultanate also helped connect different parts of the world through trade routes.
Challenges and Decline
The Seljuk Sultanate faced many challenges during its history. One major challenge was the Crusades, which were military expeditions from Europe. The Seljuks had to defend their lands against these invasions.
Later, in the 13th century, a new and powerful threat emerged: the Mongol Empire. The Mongols launched several invasions into Anatolia. In 1243, the Seljuks suffered a major defeat against the Mongols at the Battle of Köse Dağ.
After this defeat, the Seljuk Sultanate became a vassal state of the Mongols. This meant they had to obey the Mongols and pay them tribute. The Sultanate slowly lost its power and control.
The End of an Era
The Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm continued to weaken under Mongol influence. Different Seljuk princes and local leaders began to fight among themselves for power. This internal conflict made the Sultanate even weaker.
By 1308, the Seljuk Sultanate of Rûm officially collapsed. Its lands were then divided into many smaller, independent Turkish states known as Beyliks. One of these beyliks, led by a group called the Ottomans, would later grow into the mighty Ottoman Empire.
Images for kids
-
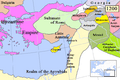
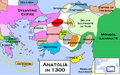
The declining Sultanate of Rûm, vassal of the Mongols, and the emerging beyliks, c. 1300
-
Hanabad caravanserai in Çardak (1230)
-
Kızıl Kule (Red Tower) built between 1221–1226 by Kayqubad I in Alanya.
See also
 In Spanish: Sultanato de Rum para niños
In Spanish: Sultanato de Rum para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |