Septum facts for kids
A septum (say: SEP-tum) is like a dividing wall or a partition that separates two spaces or parts inside something. Think of it as a barrier that keeps things apart. The word "septum" comes from Latin, meaning "something that encloses."
Contents
Septa in Your Body
Your body has many septa! They help organize different parts and keep them working correctly.
Your Nose's Septum
The nasal septum is a wall made of cartilage (a flexible material, like in your ear) and bone. It runs right down the middle of your nose, separating your two nostrils. This helps you breathe properly through both sides of your nose.
Sometimes, a nasal septum can be a bit crooked, which is called a deviated septum. This can happen from an injury, like falling or getting hit in the nose. If it's very crooked, it can make it harder to breathe through one side of your nose.
The Heart's Septum
Your heart is a powerful pump that moves blood around your body. Inside your heart, there's a strong wall called the cardiac septum. This septum divides the right side of your heart from the left side. This is super important because it keeps the oxygen-rich blood (from your lungs) separate from the oxygen-poor blood (from your body). This way, your body always gets the fresh, oxygenated blood it needs.
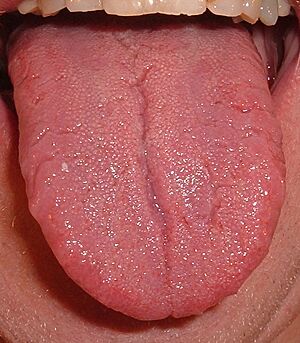
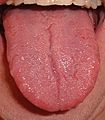
Septa in Your Tongue
Even your tongue has a septum! The lingual septum runs vertically through the center of your tongue. It helps to divide the tongue into two halves, which are mostly separate from each other. This allows the muscles on each side of your tongue to move independently, helping you speak and eat.
Septa in Animals and Plants
Septa aren't just found in humans; they appear in many other living things too!
Septa in Cephalopods
Some sea creatures, like cephalopods (think of ancient relatives of squids and octopuses, such as nautiloids and ammonites), have shells with septa. These septa are walls that divide their shells into many small chambers. These chambers help the animal control its buoyancy, allowing it to float or sink in the water.
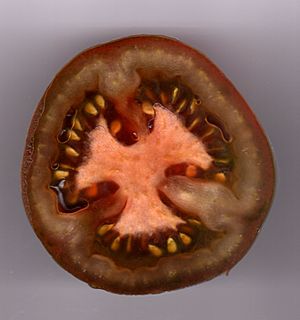
Septa in Plants
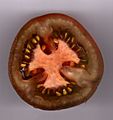
Plants also use septa. For example, if you cut open a tomato, you'll see that it's divided into sections or chambers. These dividing walls are septa, and they hold the seeds inside the fruit. Many other fruits and vegetables also have septa that separate different parts.
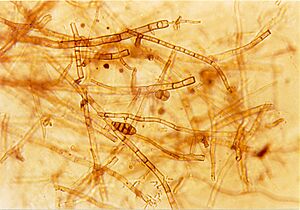
Septa in Fungi
Fungi, like mushrooms and molds, are made of tiny threads called hyphae. Many types of fungi have septa that act like little walls inside these hyphae. These septa divide the long threads into separate cells. This helps the fungus grow in an organized way and allows nutrients to move through its body.
Images for kids
-
Septins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
See also
 In Spanish: Septo para niños
In Spanish: Septo para niños