White-capped tanager facts for kids
Quick facts for kids White-capped tanager |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
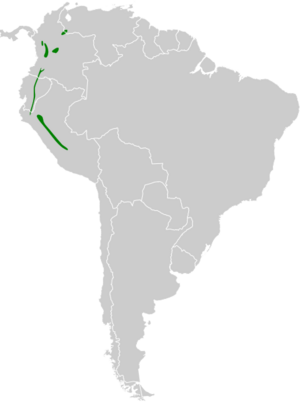 |
The white-capped tanager (Sericossypha albocristata) is a South American bird in the tanager family Thraupidae. It is the only member of the genus Sericossypha . It is the heaviest but not the longest species of tanager, at a weight of 114 g (4 oz) and a length of 24 cm (9.5 in). This species is glossy black overall with a large white crown and a red throat (which is brightest in adult males). It occurs in Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and Peru at elevations of 1600–3200 m. It lives in humid Andean forest in groups of up to 20 individuals. Flocks of these tanagers stay in tight formation, often foraging from tree to tree together. They may eat fruits, seeds, hymenoptera, and coleoptera.
Taxonomy
The white-capped tanager was formally described in 1843 by the French ornithologist Frédéric de Lafresnaye under the Latin name Tanagra (Lamprotes) albo-cristatus. The species is now the only species placed in the genus Sericossypha that was introduced in 1844 by René Lesson. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek sērikos meaning "silken" with kossuphos meaning "blackbird". The specific epithet albocristata is formed from the Latin albus meaning "white" with cristatus meaning "crested" or "plumed". The species is monotypic: no subspecies are recognised.
See also
- Magpie tanager – the longest species in the tanager family


