Sullivan Square station facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Sullivan Square
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

A northbound train departing Sullivan Square station in July 2024
|
|||||||||||
| Location | Maffa Way and Cambridge Street Charlestown, Boston, Massachusetts |
||||||||||
| Coordinates | 42°23′03″N 71°04′37″W / 42.384031°N 71.07697°W | ||||||||||
| Line(s) | Haymarket North Extension | ||||||||||
| Platforms | 2 island platforms | ||||||||||
| Tracks | 3 (Orange Line) 2 (commuter rail) |
||||||||||
| Connections | |||||||||||
| Construction | |||||||||||
| Parking | 222 spaces ($6.00 fee) | ||||||||||
| Bicycle facilities | 16 spaces | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
| Opened | June 10, 1901 (elevated station) | ||||||||||
| Rebuilt | April 7, 1975 (modern station) | ||||||||||
| Traffic | |||||||||||
| Passengers (FY2019) | 8,305 (weekday average boardings) | ||||||||||
| Services | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
Sullivan Square station is a busy train station on the MBTA subway Orange Line. It is located in the Charlestown neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. This station is a major hub where many MBTA bus routes connect. It has two island platforms for Orange Line trains. While other train lines, like the Haverhill Line and Newburyport/Rockport Line, pass through, they do not stop here.
The first train lines, the Boston and Maine Railroad (B&M) and the Eastern Railroad, opened near Sullivan Square in the mid-1800s. They both had stations here. The first fast transit station opened in 1901 as part of the Charlestown Elevated line. The current modern station opened in 1975. It was built as part of the Haymarket North Extension project. Sullivan Square station was made accessible for everyone in the 1990s.
Contents
What Does Sullivan Square Station Look Like?
Sullivan Square station is built in an open area below the Interstate 93 highway. It is just west of the Sullivan Square traffic circle. There are seven tracks in this area. Two tracks are for freight trains. Three tracks are for the Orange Line subway trains. The last two tracks are used by MBTA Commuter Rail trains.
Only two of the Orange Line tracks are used for regular service. The third Orange Line track is mostly for maintenance or testing. The station has two island platforms. One platform serves trains going in both directions. The other platform is only for northbound trains.
The station platforms are made of concrete. Above the tracks, there is a mezzanine level with a place to pay your fare. Stairs, escalators, and elevators connect the platforms to this upper level. The main entrance is on the east side of the tracks. This entrance leads to a two-level bus area. There is also a parking lot next to the bus area.
The bus area has two lanes on the lower level and one on the upper level. A walkway connects the station entrance to the lower bus area. Sullivan Square is a very important MBTA bus hub. Many bus routes, like 86,andCT2, stop here.
History of Sullivan Square Station
Early Railroad Stations
The Boston and Maine Railroad (B&M) opened its main line near Sullivan Square in 1845. Another line, the Eastern Railroad, started passenger service here in 1854. Both railroads soon opened stations at Sullivan Square. These stations were sometimes called Somerville or East Somerville. Even though they were in Charlestown, they mostly served nearby Somerville.
By 1875, the B&M station was north of Cambridge Street. The Eastern station was south of it. The B&M bought the Eastern Railroad in 1885. They continued to use both stations for a while.
Crossing Cambridge Street was dangerous because so many trains crossed it every day. In 1895, electric streetcars were added to the street. They had to take long detours to avoid the train tracks. To make the area safer, a project began in 1900. Cambridge Street was raised onto a bridge over the tracks.
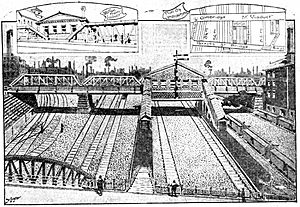
As part of this project, the B&M built a new East Somerville station. This new station building was located over the tracks. It had two island platforms that you could reach by stairs. The station opened in June 1901. The Cambridge Street bridge was finished in July of that year.
The station building closed in 1927 because fewer people were taking short train trips. It was soon torn down. By 1932, very few trains stopped there. The station officially closed on May 16, 1958. This was part of a big change where many local train services were stopped.
The Old Elevated Station
The first fast transit station at Sullivan Square opened on June 10, 1901. It was part of the Charlestown Elevated line. This line was an early version of today's Orange Line. The original elevated station was very impressive. It was made of steel and brick. It had a large glass roof over an open area inside.
Sullivan Square and its station are named after James Sullivan. He was a governor of Massachusetts in the early 1800s. He was also the first president of the Middlesex Canal Company.
The station was built to be a major transfer point. Many streetcar lines that used to go downtown now ended at Sullivan Square. Streetcars could go up a ramp to ten tracks at the same level as the elevated trains. This allowed people to easily switch between streetcars and trains. Some streetcar lines that didn't end here used a loop at ground level. Streetcars continued to serve the station until 1955.
Over time, the old Charlestown Elevated line and Sullivan Square station became worn out. A large fire damaged the station in 1967. The Charlestown Elevated line closed on April 4, 1975. Some people wanted to save the old station and fix it up. However, the station was eventually torn down starting in March 1976.
The Modern Station Today
The Haymarket North Extension was a new train line built in the early 1970s. It followed the path of the Haverhill Line tracks. The new Sullivan Square station was built under the I-93 highway. The Haymarket North Extension opened to Sullivan Square on April 7, 1975. The new Sullivan station was the end of the line for five months. Then, the [[{{{station}}} (MBTA station)|{{{station}}}]] station opened on September 6, 1975.
When it first opened, Sullivan station was not accessible for people with disabilities. Elevators were added to the station in 1991–1992. In 2002, the MBTA added art panels by local schoolchildren to the station. The concrete walls of the station are often covered with large graffiti art.
From 2018 to 2019, the station's bus areas were updated. This project was funded partly because of the new Encore Boston Harbor casino nearby. The lower bus area was divided into two lanes. A new exit to Cambridge Street was added for buses. The Orange Line, including Sullivan Square station, was closed for maintenance from August 19 to September 18, 2022.
Future Plans
Sullivan Square was once considered for the Urban Ring. This was a plan for a fast bus line that would connect different MBTA train lines. The idea was to make it easier to travel around Boston without going through downtown. This project was canceled in 2010. In March 2024, the MBTA announced plans to extend the Silver Line route SL3 to Sullivan Square.
There are also plans to improve accessibility at Sullivan Square. A project is designed to add and replace elevators at the station. This will include a new elevator to the lower bus area.
A study in 2013 suggested building new things over the station's parking lot and bus areas. This could include parking garages, shops, and even offices.
See also
 In Spanish: Sullivan Square (Metro de Boston) para niños
In Spanish: Sullivan Square (Metro de Boston) para niños