Surface condenser facts for kids
A surface condenser is a super important machine used in places like power stations. Imagine a big engine that uses steam to make electricity. After the steam does its job, the condenser steps in to cool it down and turn it back into water. This way, the water can be used again and again, which saves a lot of resources!
Contents
How a Condenser Works
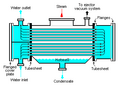
A surface condenser is a special type of heat exchanger. This means it moves heat from one place to another. In a power station, hot steam from a steam turbine enters the condenser. Inside, there are many tubes filled with cool water, usually from a river, lake, or cooling tower.
The Cooling Process
When the hot steam touches the cool tubes, it quickly loses its heat. This causes the steam to change from a gas back into liquid water. This process is called condensation. The cool water inside the tubes gets warmer as it absorbs the heat from the steam.
Why Condensation is Important
Turning the steam back into water is very important for a few reasons:
- Reusing Water: It allows the same water to be used over and over again in the power station's boiler. This saves a lot of fresh water.
- Efficiency: It creates a very low-pressure area (a vacuum) at the end of the steam turbine. This low pressure helps the turbine work more efficiently and produce more electricity.
Where Condensers Are Used
Surface condensers are mostly found in large power stations that use steam to generate electricity. These include:
- Coal-fired power plants: Where coal is burned to heat water into steam.
- Nuclear power plants: Where nuclear reactions create heat for steam.
- Geothermal power plants: Using heat from the Earth to make steam.
They can also be used in other industrial settings where steam needs to be condensed back into water for various processes.
Images for kids
 | Dorothy Vaughan |
 | Charles Henry Turner |
 | Hildrus Poindexter |
 | Henry Cecil McBay |