Tedbury Camp facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Tedbury Camp |
|
|---|---|
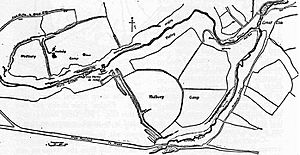
Plan of the site
|
|
| Location | Great Elm, Somerset, England |
| Area | c. 60 acres (24 ha) |
| Built | Iron Age |
| Reference no. | 202769 |
| Lua error in Module:Location_map at line 420: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value). | |
Tedbury Camp is an ancient fort from the Iron Age in Somerset, England. It's known as a "hill fort" because it was built on a hill. This special type of fort is called a "promontory hill fort" because it sits on a piece of land that sticks out, with steep slopes on two sides. It was protected by two strong, parallel earth walls.
Contents
Tedbury Camp: An Ancient Fort
Tedbury Camp is a very old site. It was built during the Iron Age, a time when people started using iron tools. This period began around 3,000 years ago.
What is a Hill Fort?
Hill forts are large, walled settlements built on hills. They were common in Britain during the Late Bronze Age and Early Iron Age. People built them for different reasons.
Some experts think they were military sites. They might have been built to defend against invaders. Others believe they were places for communities to gather. They could have been safe spots when there was conflict.
The use of iron changed society a lot. New trade routes formed, and power shifted. Hill forts offered protection during these changing times. They were not always used for war, but they could be.
Exploring Tedbury Camp
Tedbury Camp covers about 60 acres (24 hectares). This is a very large area. It sits between two rivers, the Mells River and Fordbury Water.
The fort has impressive defenses. Its inner earth wall is quite big. It measures about 4 to 6 feet (1.2 to 1.8 meters) wide. In some places, it stands 10 to 15 feet (3 to 4.5 meters) high. There might have even been a third wall at one point.
Roman History at the Camp
Tedbury Camp was also used by the Romans. They occupied the site between the years 337 and 366 AD. In 1691, a collection of Roman coins was found here. These coins belonged to a Roman emperor named Constantine Junior.
People have explored Tedbury Camp more recently too. During the 19th and 20th centuries, more digs took place. Between 1939 and 1945, a Quern-stone was discovered. A quern-stone is a tool used for grinding grain.
About 500 meters (1,640 feet) northeast of the camp, there was a quarry. This quarry dug up a type of rock called Carboniferous Limestone. This area also shows a cool geological feature. It's called an "angular unconformity." This is where layers of rock are tilted at different angles. It shows how the Earth's crust has moved over millions of years.
 | Aaron Henry |
 | T. R. M. Howard |
 | Jesse Jackson |


