Common blanket octopus facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Common blanket octopus |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
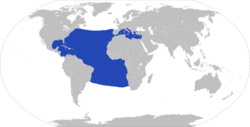
| Range of Tremoctopus violaceus | |
| Synonyms | |
|
The common blanket octopus or violet blanket octopus (Tremoctopus violaceus) is a fascinating sea creature. It is a type of large octopus that lives in warm oceans around the world. You can find it in the open ocean, near the surface.
One of the most amazing things about this octopus is how different males and females are in size. Females can grow up to two meters (about 6.5 feet) long. But males are tiny, only about 2.4 centimeters (less than an inch) long! This means a female can be 10,000 times heavier than a male. Scientists didn't even see a live male until 2002, near the Great Barrier Reef.
Young males and smaller females (less than 7 cm) have a clever trick. They carry tentacles from the Portuguese man o' war. These tentacles are known for their strong stings. Scientists think the octopuses use them for defense and to catch food. Once they get bigger, this trick isn't as useful. This might be why the males stay so small.
The adult female octopus has a special web between her arms. This web can spread out like a blanket, making her look much bigger. If a predator tries to bite her web, she can easily let go of that part. This helps her escape.
-
Lateral view of adult male with hectocotylus
Reproduction and Mating
When it's time to reproduce, the male blanket octopus uses a special arm. This arm is called the hectocotylus. It holds what the male needs for mating.
When the male is ready, he releases the contents of this arm. He then breaks off the arm and gives it to the female. After this, it's likely the male dies. The female keeps this arm inside her body. She can store several arms from different males. She uses them later when she is ready to lay her eggs.
Why Males and Females are So Different in Size
The common blanket octopus shows one of the biggest size differences between males and females in the animal kingdom. There are a few ideas why this happens:
- Big Females are Better: Female octopuses need a lot of energy to make and carry their eggs. The bigger a female is, the more eggs she can produce. This means more baby octopuses might survive.
- Small Males are Fine: Males don't need as much energy or space for their part in reproduction. So, there's no pressure for them to be big.
- Staying Safe: Using the stinging tentacles of the Portuguese man o' war only works for smaller octopuses. So, it might be that males stayed small because it helps them keep this defense strategy. This is a good example of natural selection at work.
Defense Strategies
The common blanket octopus has several ways to protect itself from predators. Its enemies include the blue shark, tuna, and billfish.
- The Blanket Web: Female blanket octopuses can quickly roll up or spread out their webbed "blanket." This blanket makes the octopus look much larger and more intimidating. If a predator bites the web, the female can easily detach that part. This distracts the predator and allows her to escape.
- Portuguese Man O' War Tentacles: Male blanket octopuses and smaller females use the stinging tentacles of the Portuguese man o' war. They attach these tentacles to their four top arms. It's not fully known if the octopus is immune to the man o' war's venom or if they just hold the stingers in parts of their body that aren't sensitive. These stinging tentacles are useful for both defense and hunting. They can scare away predators and also help the octopus catch its own food.