Blue shark facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Blue shark |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: |
Prionace
Cantor, 1849
|
| Binomial name | |
| Prionace glauca (Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
 |
|
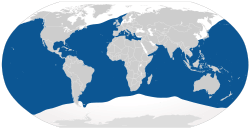
| Range of the blue shark | |
The blue shark (Prionace glauca) is a type of requiem shark. It has a sleek, smooth body with big eyes and a long, cone-shaped snout. Its back is a dark blue color, and its belly is white.
The biggest blue sharks can grow up to 3.8 meters (12.5 feet) long. They can weigh as much as 206 kilograms (454 pounds). This shark lives all over the world in both temperate (mild) and tropical (warm) waters. They can be found from the ocean surface down to 350 meters (1,148 feet) deep. They like water that is between 7 and 16 °C (45-61 °F).
Contents
What Does a Blue Shark Look Like?
The blue shark has a sleek, smooth body. It has large eyes and a long, cone-shaped snout. This snout is longer than the width of its mouth. It has very long, pointed pectoral fins (side fins). These fins are usually as long as the distance from its snout to its gills.
Its dorsal fin (top fin) is a medium size. It is closer to the pelvic fins (belly fins) than to the pectoral fins. The blue shark gets its name from its dark blue back and bright blue sides. Its belly is white. These colors help the blue shark hide in the open ocean.
The largest blue shark ever recorded was 3.8 meters (12.5 feet) long. Some people say they can grow up to 6.1 meters (20 feet). Male sharks become adults at 4–5 years old. At this age, they are about 1.8-2.8 meters (6-9.2 feet) long. Females become adults a bit later, at 5–6 years old. They are about 2.2-3.2 meters (7.2-10.5 feet) long when they mature. The heaviest blue sharks weigh between 204–206 kg (450-454 pounds).
Where Do Blue Sharks Live?
Blue sharks live all around the world. They are found in both temperate and tropical waters. They are a pelagic species. This means they live in the open ocean and rarely come close to shore. However, they sometimes swim near oceanic islands. They also visit places where the continental shelf is narrow.
In the western Atlantic, they live from Newfoundland, Canada to Argentina. In the eastern Atlantic, they range from Norway to South Africa. This includes the Mediterranean. In the Indian Ocean, they are found from South Africa to Indonesia. In the western Pacific, they live from Japan to New Zealand. In the eastern Pacific, blue sharks are found from the Gulf of Alaska to Chile.
Since they are a pelagic species, blue sharks live in open ocean areas. They can be found from the surface down to 350 meters (1,148 feet) deep. They prefer cooler water, usually between 7 and 16 °C (45-61 °F). They have been seen in warmer water, up to 21 °C (70 °F) or more. When they are in tropical areas, they usually swim to deeper, cooler water. For example, in the tropical Indian Ocean, most blue sharks are found at depths of 80–220 meters (263–722 feet). Here, water temperatures are 12-25 °C (54-77 °F).
In the Pacific, between 20°N and 50°N latitudes, they travel to cooler northern areas in summer. They move to warmer southern areas in winter. Their numbers stay steady throughout the year between 20°N and 20°S latitude.
How Do Blue Sharks Behave?
Blue sharks can live in a wide range of water depths. They can be found from the surface all the way to the bottom. This helps them find food easily. Blue sharks are known to travel thousands of miles to find food and to mate.
These sharks often live in groups. These groups are usually made up of sharks of the same gender and size. They are sometimes called the "Wolves of the Sea." This is because they form complex social groups, much like wolves. Divers need to be careful around them because they can be territorial and act aggressively. Many videos of these sharks are filmed with divers inside protective cages for safety.
What Do Blue Sharks Eat?
Most of what blue sharks eat are invertebrates. These include squid, cuttlefish, and open-ocean octopus. They also eat bony fish like herring and sardines. They also feed on different types of sea birds. Their diet also includes crustaceans like lobster, crab, and shrimp. They also eat dead animals, which is called carrion.
Blue sharks are very good at finding food. They are known to eat almost anything they can find. This includes prey that is available in large numbers, like shrimp. They have been known to eat until they cannot eat any more. Because they eat almost anything, they sometimes swallow garbage and rubbish. This includes things like plastic and rubber tires. Eating these items can make the shark sick and even cause it to die.
How Do Blue Sharks Reproduce?
Blue sharks are viviparous. This means they give birth to live young, rather than laying eggs. Males become adults at 4-5 years old. Females become adults at 5-6 years old. The pregnancy lasts from 9 to 12 months.
During mating, male sharks sometimes bite the females. However, the female's thick skin is thought to prevent any pain. Baby sharks, called pups, are 41 to 50 cm (16 to 20 inches) long when they are born. Females can give birth to anywhere from 4 to 135 pups at a time. The number of pups depends on the size of the female shark. Larger females tend to have more pups. Blue sharks can live for up to 20 years.
Who Are the Blue Shark's Predators?
Larger animals that hunt blue sharks include the California sea lion. Other bigger sharks also prey on them. These include the Shortfin mako shark and the Great white shark.
How Do Humans Interact with Blue Sharks?
For fun, blue sharks are seen as a sport fish. Large ones offer a challenge for people who like to fish. Most blue sharks caught by commercial fishing boats are caught by accident. This is called "bycatch." It is thought that 10 to 20 million blue sharks are killed each year. This might be harming their populations around the world.
Blue sharks sometimes eat fish caught by salmon, mackerel, and sardine fisheries. They also get tangled in fishing nets. The fins of blue sharks are sold to markets in Asia. They are used to make shark-fin soup.
Blue sharks are considered a species that needs to be approached with caution. They have been known to attack humans and boats. The International Shark Attack File (ISAF) has recorded twelve unprovoked attacks on humans. They have also recorded four attacks on boats. Three recorded attacks happened after air or sea disasters. There are also stories of blue sharks attacking sailors who were shipwrecked in the open ocean. A blue shark might circle swimmers or divers for fifteen minutes or more. While they are not always aggressive, they are not shy. It is important to be careful around them, especially if they are circling. They might try to bite.
How Are Blue Sharks Protected?
Blue sharks are one of the most common and widespread sharks. They also grow quickly. However, they are also one of the most heavily fished sharks in the world. An estimated 10 to 20 million blue sharks are caught and killed each year. People are worried about what this means for blue shark populations. They are also concerned about what removing such an important predator might do to the ocean's ecosystem.
Blue sharks are very important in the international trade of shark fins. Their meat is eaten in a few countries, but it is not very popular. The IUCN lists the blue shark as Near Threatened. This means they could become endangered in the future.
[1]
- Blue shark, Prionace glauca MarineBio"
- Blue shark, Prionace glauca at the Encyclopedia of Life
- ARKive - Images and movies of the blue shark (Prionace glauca)
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Tintorera para niños
In Spanish: Tintorera para niños








