Blue-naped mousebird facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Blue-naped mousebird |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Genus: |
Urocolius
|
| Species: |
macrourus
|
| Synonyms | |
|
Lanius macrourus Linnaeus, 1766 |
|
The blue-naped mousebird (Urocolius macrourus) is a unique bird. It belongs to the Coliidae family. This family is part of the Coliiformes group. These birds are special because they are related to many other bird groups. These include cuckoo rollers, trogons, hornbills, hoopoes, woodpeckers, toucans, barbets, kingfishers, bee-eaters, rollers, motmots, and todies.
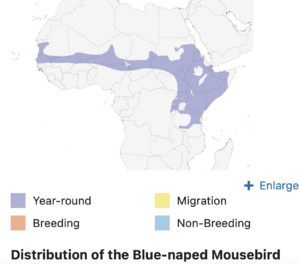
You can find the blue-naped mousebird in dry areas of West Africa to East Africa. They also live in the Sahel region. There are only six types of mousebirds left. The name "mousebird" comes from how they move. They run along branches like a mouse scurrying.
Contents
What are the different types?
There are six recognized types, or subspecies, of the blue-naped mousebird. These different types live in various parts of Africa.
- Urocolius macrourus macrourus (Found from Senegambia to east Ethiopia)
- Urocolius macrourus syntactus (Found in the Sahel region, from Mali to Sudan and Eritrea)
- Urocolius macrourus laeneni (Found in the Aïr Massif in central Niger)
- Urocolius macrourus pulcher (Found in South Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia, and Tanzania)
- Urocolius macrourus abyssinicus (Found in Central and Southern Ethiopia, and Northern Somalia)
- Urocolius macrourus griseogularis (Found in South Sudan, Congo, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, and Tanzania)
What do they look like?
The blue-naped mousebird is a small to medium-sized bird. It is about 33 to 38 centimeters (13 to 15 inches) long. This includes its very long tail, which is 20 to 28 centimeters (8 to 11 inches) long. It weighs between 34 and 65 grams (1.2 to 2.3 ounces).
Adult birds are mostly ash grey. They are darker on top and lighter underneath. They have a bright turquoise-blue patch on their neck. They also have a long crest on their head. Females usually have shorter tails than males. Both male and female birds have reddish skin around their eyes. Their upper beak is also reddish, and the rest of their beak is black. Their feet are purplish-red.
Young blue-naped mousebirds look a bit different. They do not have the blue patch on their neck. Their face skin is pink, and their beaks are greenish. Their crests are also shorter.
Mousebirds have special feet. Their feet are large for their body size. They can turn all four toes forward. This helps them climb and move along branches easily. They can even hang by one toe! They also use their strong toes to hold food.
Where do they live?
Blue-naped mousebirds live in dry and semi-desert areas of Africa. In East Africa, they are found in a wide band. This band stretches from the western coast to countries like Sudan, Ethiopia, and Somalia. They also live further south in East Africa.
These birds have a very large natural home range. This means they are not considered to be in danger of disappearing.
Are they in danger?
The number of blue-naped mousebirds seems to be going down. However, this decline is not happening fast enough to be a major concern. Scientists believe there are still many of these birds. Because of this, their conservation status is "Least Concern." This means they are not currently at risk of extinction.
How do they behave?
What sounds do they make?
When a blue-naped mousebird is alone on a tree, it makes a clear "tieee" whistle. It repeats this sound every 3 to 5 seconds. When it is looking for food, the call is shorter and softer. It makes this call every 10 to 15 seconds.
When many mousebirds are together, they make different sounds. Before flying, they might make a "trie-trie" sound. Just before taking off, they make a rhythmic "tsie-tsie..." sound. In flight, their calls change to "trui-tru-tri" or "triu-triu."
During courtship, a female might make a special "cruir-uu-tuit-truit" sound. The male will respond with "tiuee-tuiee..." notes. Sometimes, perched birds also make soft trills.
How do they move around?
Blue-naped mousebirds usually stay in one area. But sometimes, they move to new places. This often happens during the dry season. They might move from woodlands to river valleys or towns. These movements explain why they are sometimes seen in places like Benin or Gambia.
What do they eat?
These birds mainly eat fruits. They also enjoy leaves, flowers, and buds. They often look for food together in groups. In some areas, like Niger, they especially like the berries of the Salvadora persica plant. They also eat fruits from other plants like Balaenites aegyptiaca and Ficus. They even eat dates and fruits from cultivated trees, like the Azadirachta indica tree found in towns.
You can often see these birds in groups of up to ten. Sometimes, as many as 50 birds gather around one fruit tree. They travel in flocks from one fruit tree to another. They stop to eat every 20 to 200 meters. They often follow the same path at the same time each day.
How do they raise their young?
Blue-naped mousebirds can breed all year round. The busiest breeding time is usually during or right after the rainy seasons. For example, it's May to June in Nigeria and April to July in Ethiopia.
In zoos, these birds often stay with one partner for a long time. They probably defend their nesting area in the wild. The nest is a shallow, messy cup. It is made of twigs and lined with grass and roots. The male brings materials, and the female builds the nest. Nests are usually in a tree or thorny bush, about 3 to 4.5 meters (10 to 15 feet) off the ground.
A female usually lays 2 to 3 eggs, but sometimes 1 to 4. The eggs are whitish with reddish or brown spots. They are about 20.3 mm by 14.5 mm in size. Both parents take turns sitting on the eggs. The female sits at night, and the male sits during the day.
How do the chicks grow?
The eggs hatch in about 11 days. A newly hatched chick weighs around 2.3 grams. They have special swellings on their lower beak. These disappear after about a month. Chicks may leave the nest when they are 10 to 12 days old. At this age, they are about half the size of an adult.
Their first flight happens around 16 to 17 days old. But they still return to the nest until they are 21 days old. They depend on their parents for food for about six more weeks. They reach their full adult size around 15 weeks old. In captivity, some blue-naped mousebirds have lived for over 11 years.
Gallery