Western African Ebola epidemic facts for kids
Simplified Ebola virus epidemic situation map
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Date | December 2013 – June 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Quick facts for kids Casualties |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The 2013–2016 epidemic of Ebola virus disease was a very serious health crisis. It mainly affected Western Africa. This was the largest Ebola outbreak ever recorded.
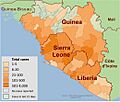
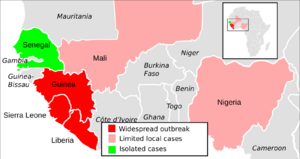
The disease caused many deaths and big problems for the economy and daily life in the region. The countries hit hardest were Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone.
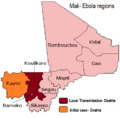
The first cases were found in Guinea in December 2013. From there, it spread to nearby Liberia and Sierra Leone. Smaller outbreaks also happened in Nigeria and Mali. A few medical workers got sick in the United States and Spain. Single cases were also reported in Senegal, the United Kingdom, and Italy.
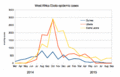
The number of cases was highest in October 2014. After many countries sent help, the numbers slowly started to go down.
Contents
Understanding the Ebola Outbreak
The Ebola outbreak caused many people to die. It had a high case fatality rate, which means a large percentage of infected people died.
By the end of the epidemic, about 28,616 people had been infected. Sadly, 11,310 of them died. This means about 40% of those infected passed away. The World Health Organization (WHO) believed the actual numbers were much higher.
On August 8, 2014, the WHO declared a "Public Health Emergency of International Concern." This meant the outbreak was a serious global threat. The emergency status ended on March 29, 2016. The epidemic was finally declared over on June 9, 2016. This was 42 days after the last known patient tested negative for the virus.
Life After Ebola: Survivors and the Virus
About 17,000 people survived the disease. Many of them experienced long-lasting health problems. These are called post-Ebola syndrome. These symptoms can be severe and need medical care for months or even years.
Scientists also found that the virus can sometimes "hide" in a survivor's body. It can then become active again months or even years later. This was a big concern.
In December 2016, the WHO announced good news. A two-year study showed that the rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine could protect people from the type of Ebola virus in this outbreak. This vaccine is very effective. About 300,000 doses have been stored for future use. The rVSV-ZEBOV vaccine was officially approved in 2019.
How the Outbreak Spread
The Ebola virus spread quickly in West Africa. It moved from Guinea to Liberia and Sierra Leone. The virus then traveled to other countries through people who were infected.
- Guinea: This is where the outbreak started in December 2013.
- Liberia: The virus spread here from Guinea.
- Sierra Leone: This country also saw many cases after the virus spread from its neighbors.
Smaller Outbreaks in Other Countries
While Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone had the most cases, other countries also saw some infections. These were usually smaller outbreaks.
- Nigeria: Had 20 cases and 8 deaths. The outbreak ended in October 2014.
- Mali: Had 8 cases and 6 deaths. The outbreak ended in January 2015.
- United States: Had 4 cases and 1 death, mostly involving medical workers.
- Spain: Had 1 case, also a medical worker.
- Senegal, United Kingdom, Italy: Each had one case.
These smaller outbreaks showed how quickly the virus could travel. However, quick actions helped stop them from spreading widely.
See also
- Health crisis
Images for kids
 | Calvin Brent |
 | Walter T. Bailey |
 | Martha Cassell Thompson |
 | Alberta Jeannette Cassell |