Whyte notation facts for kids
The Whyte notation is a cool way to classify steam locomotives (trains that run on steam!) based on how their wheels are arranged. Think of it like a secret code that tells you how many wheels a train has and where they are. This system was created by a person named Frederick Methvan Whyte. It became popular in the early 1900s, especially after a magazine called American Engineer and Railroad Journal encouraged its use.
Contents
What is Whyte Notation?
Whyte notation uses numbers to describe the wheels on a steam locomotive. It focuses on three main groups of wheels:
- The wheels at the very front of the locomotive, called the leading wheels. These wheels help guide the train around curves.
- The big wheels in the middle, called the driving wheels. These are the wheels that are connected to the engine and make the train move forward.
- The wheels at the back, called the trailing wheels. These wheels support the back of the locomotive and its heavy firebox.
How to Read the Numbers
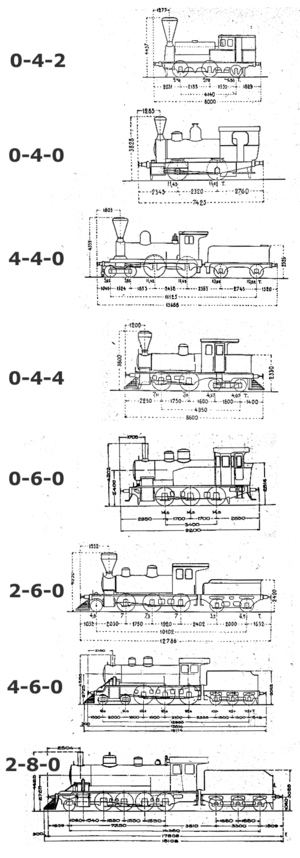
The notation is written as three numbers, separated by dashes. For example, a locomotive might be called a "4-4-0".
- The first number tells you how many leading wheels the locomotive has.
- The second number tells you how many driving wheels it has.
- The third number tells you how many trailing wheels it has.
So, a 4-4-0 locomotive has 4 leading wheels, 4 driving wheels, and 0 trailing wheels.
Why is it Important?
This system helps people quickly understand a locomotive's design. Different wheel arrangements were good for different jobs:
- Some were built for speed.
- Others were designed to pull very heavy loads.
- Some were better for climbing steep hills.
Knowing the Whyte notation helps train enthusiasts and engineers identify a locomotive's purpose and capabilities.
Common Whyte Notation Examples
Many famous steam locomotives have specific Whyte notations. Here are a few examples:
The 4-4-0 "American"
The 4-4-0 was one of the most common types of locomotives in the United States during the 19th century.
- It had 4 leading wheels, 4 driving wheels, and no trailing wheels.
- It was known for being fast and reliable for passenger trains.
The 2-8-0 "Consolidation"
The 2-8-0 was a very popular freight locomotive.
- It had 2 leading wheels, 8 driving wheels, and no trailing wheels.
- The 8 driving wheels gave it a lot of power to pull heavy goods trains.
The 4-6-2 "Pacific"
The 4-6-2 was often used for express passenger services.
- It had 4 leading wheels, 6 driving wheels, and 2 trailing wheels.
- The trailing wheels helped support a larger firebox, which meant more steam and more power for speed.
The 4-8-4 "Northern"
The 4-8-4 was a powerful, all-around locomotive.
- It had 4 leading wheels, 8 driving wheels, and 4 trailing wheels.
- These locomotives were very versatile and could handle both passenger and freight duties.
How Whyte Notation Helps Today
Even though steam locomotives are not as common now, the Whyte notation is still used by historians, model train builders, and railway enthusiasts. It helps them talk about and understand these amazing machines from the past. It's a simple yet powerful system that has stood the test of time!
See also
 In Spanish: Notación Whyte para niños
In Spanish: Notación Whyte para niños