Acromegaly facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Acromegaly |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
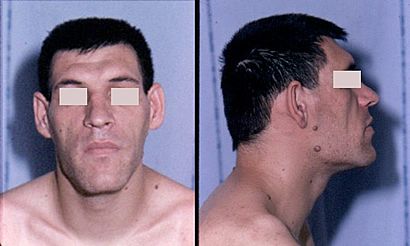
| Facial features of a person with acromegaly. The cheekbones are pronounced, the forehead bulges, the jaw is enlarged, and facial lines are prominent. | |
| Symptoms | Enlargement of the hands, feet, forehead, jaw, and nose, thicker skin, deepening of the voice |
| Complications | Type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, high blood pressure |
| Usual onset | Middle age |
| Causes | Too much growth hormone |
| Diagnostic method | Blood tests, medical imaging |
| Treatment | Surgery, medications, radiation therapy |
| Medication | Somatostatin analogue, GH receptor antagonist |
| Prognosis | Usually normal (with treatment), 10 year shorter life expectancy (no treatment) |
| Frequency | 6 per 100,000 people |
Acromegaly is a health problem where your body makes too much growth hormone. This happens after your bones have finished growing. It often makes your hands and feet get bigger. Your forehead, jaw, and nose might also grow larger. Other signs can include joint pain, thicker skin, and a deeper voice. You might also get headaches or have problems with your vision.
Sometimes, acromegaly can lead to other health issues. These include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea (where you stop breathing for short times while sleeping), and high blood pressure.
Contents
What Causes Acromegaly?
Acromegaly usually happens because of a small, harmless growth. This growth is called a benign tumor. It forms on your pituitary gland, which is a tiny gland in your brain. The pituitary gland normally makes growth hormone. But with this tumor, it makes too much. More than 95% of acromegaly cases are caused by these tumors.
Acromegaly is not something you get from your parents. It's not inherited. Very rarely, it can be caused by a tumor in another part of the body.
How Doctors Find Acromegaly
Doctors can find acromegaly with blood tests. They might measure your growth hormone levels after you drink a special sugar solution. Or they might check a substance called insulin-like growth factor I in your blood.
After a diagnosis, doctors use medical imaging (like an MRI scan) to look at your pituitary gland. This helps them see if a tumor is there. If a child makes too much growth hormone, they get a condition called gigantism, not acromegaly. This is because their bones are still growing.
Treating Acromegaly
There are different ways to treat acromegaly. The most common treatment is surgery to remove the tumor. Surgery works best when the tumor is small.
If surgery isn't an option or doesn't fully work, doctors might use medications. These medicines can help lower the amount of growth hormone your body makes. Sometimes, radiation therapy is also used. This treatment uses special rays to shrink the tumor.
With good treatment, many symptoms get much better or even go away. This includes headaches, vision problems, and diabetes. Swelling in soft body parts usually goes down. Also, the changes in your face from acromegaly can slowly return to normal. If acromegaly is treated early and successfully, people can live a normal lifespan. Without treatment, life expectancy can be shorter.
Who Gets Acromegaly?
About 6 out of every 100,000 people have acromegaly. It's most often found in middle-aged adults. Both males and females get it equally. The condition was first described by a doctor named Nicolas Saucerotte in 1772.
The word "acromegaly" comes from Greek words. Akron means "extremity" (like hands and feet), and mega means "large."
Signs of Acromegaly
When you have too much growth hormone or a growing tumor, you might notice these signs:
- Headaches: You might get bad headaches that last a long time.
- Bigger body parts: Your hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears might get bigger. Your skin can also get thicker.
- Changes inside: Your vocal cords might swell, making your voice thick and deep. You might also speak slower.
- Skull changes: Your skull might get bigger, especially your forehead.
- Jaw and mouth changes: Your lower jaw might stick out more. Your tongue might get bigger, and your teeth might spread apart.
- Skin tags: You might get small, soft growths on your skin called skin tags.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome: This is when a nerve in your wrist gets squeezed, causing pain or numbness in your hand.
Images for kids
-
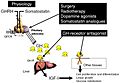
This picture shows where different treatments work. Surgery, radiotherapy, and some medicines act on the pituitary adenoma (the tumor). Other medicines block the effects of growth hormone in the body.
See also
 In Spanish: Acromegalia para niños
In Spanish: Acromegalia para niños