Pituitary adenoma facts for kids
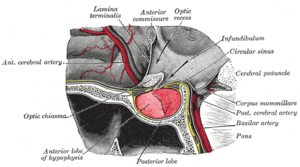
The pituitary gland is a tiny but super important part of your brain. It's like the master controller for many hormones in your body! Sometimes, a small growth can appear on this gland. These growths are called pituitary adenomas. Most of the time, these growths are not cancer and are quite harmless.
Scientists usually group pituitary adenomas into three main types:
- Benign adenomas: These are the most common type. They are usually harmless and do not spread to other parts of the body.
- Invasive adenomas: These growths can spread a little into nearby areas, like the bones around the brain.
- Carcinomas: These are very rare and are a type of cancer. They make up a tiny fraction of all pituitary growths.
Pituitary adenomas are actually quite common. They are found in about 10% to 25% of all brain growths. It's thought that about 17% to 25% of people might have one, often without even knowing it!
What Are Macroadenomas and Microadenomas?
Pituitary adenomas are also named based on their size:
- Macroadenomas: These are growths that are bigger than 10 mm (about the size of a large pea).
- Microadenomas: These are smaller growths, less than 10 mm.
Most pituitary adenomas are microadenomas. Many microadenomas are so small that they don't cause any problems. They are often found by chance when someone has a brain scan for a different reason. When they are found this way, they are sometimes called incidentalomas. This just means they were found "incidentally" or by accident.
Where Can They Spread?
Even though most pituitary adenomas are harmless, some invasive adenomas can spread a little. They might grow into the tough outer layer covering the brain (called the dura mater), or into the bones of the skull nearby. This includes a bone called the sphenoid bone, which is at the base of your skull.
It was once thought that these growths causing symptoms were very rare. However, newer studies suggest that about one in 1000 people might have a pituitary adenoma that causes noticeable problems.
Images for kids
-
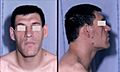
Morphological facial changes caused by acromegaly; frontal bossing, enlarged nose, prognathism and maxillary widening with separation of teeth and unseen, enlargement of the tongue (macroglossia).
See also
 In Spanish: Tumor de hipófisis para niños
In Spanish: Tumor de hipófisis para niños