Adenoid facts for kids
Adenoids (also called pharyngeal tonsils or nasopharyngeal tonsils) are special groups of tissues found at the very back of your nose. They are located in the part of the nose that connects to the back of your mouth and throat. In most children, adenoids form a soft bump on the top and back section of the air passage in the nose. They are an important part of your body's immune system, helping to fight off germs.
Contents
What Are Adenoids?
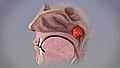
Adenoids are a type of lymphoid tissue, similar to your tonsils. They are located high up in the nasopharynx, which is the upper part of your throat behind your nose. Unlike tonsils, you cannot easily see adenoids by just opening your mouth. Doctors usually need special tools to view them.
What Do Adenoids Do?
Your adenoids play a role in your immune system. They help to trap germs like bacteria and viruses that you breathe in. When they catch these germs, they produce antibodies to help your body fight off infections. This is especially important when you are a young child.
When Adenoids Cause Problems
Sometimes, adenoids can become enlarged or swollen. This is often called adenoid hypertrophy. When they get too big, they can block the air passage in the nose. This can lead to several health issues, especially for children.
Signs of Enlarged Adenoids
If a child's adenoids are too large, you might notice some common signs:
- Difficulty breathing through the nose: They might breathe mostly through their mouth, especially at night.
- Snoring: Loud snoring is common, and sometimes even sleep apnea, where breathing stops for short periods during sleep.
- Frequent ear infections: Enlarged adenoids can block the tubes that connect the middle ear to the back of the nose. This can cause fluid buildup and ear infections.
- Nasal voice: Their voice might sound "stuffy" or like they have a constant cold.
- Chronic runny nose: They might have a persistent runny nose or nasal congestion.
Why Adenoids Get Big
Adenoids can become enlarged for several reasons. Often, repeated infections, like common colds or allergies, can cause them to swell. Sometimes, they are just naturally larger in some children. They usually shrink on their own as children get older, often disappearing by the time a person reaches their teens.
Treating Adenoid Problems
If enlarged adenoids cause significant health problems, a doctor might suggest treatment. This could involve medicines to reduce swelling or, in some cases, surgery.
What is an Adenoidectomy?
Taking away adenoids with surgery is called an adenoidectomy. This is a common and safe surgical procedure. It is usually done by an otolaryngologist, which is a doctor who specializes in ear, nose, and throat problems. The surgery is typically quick, and children can often go home the same day.
When is Surgery Needed?
Doctors usually recommend an adenoidectomy if a child has:
- Severe breathing problems, especially during sleep.
- Very frequent ear infections that affect hearing.
- Ongoing sinus infections that don't get better with other treatments.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Amígdala faríngea para niños
In Spanish: Amígdala faríngea para niños