Parachuting red-eyed leaf frog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Parachuting red-eyed leaf frog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
| Synonyms | |
|
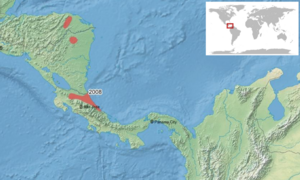
The Agalychnis saltator, also known as the parachuting red-eyed leaf frog or misfit leaf frog, is a special type of frog. It belongs to the leaf frog family. You can find this frog in the lowlands of the Caribbean. Its home stretches from north-eastern Honduras to eastern-central Costa Rica. These frogs live at different heights, from about 15 to 1300 meters above sea level.
Contents
About the Parachuting Red-Eyed Leaf Frog
Male Agalychnis saltator frogs are about 38 to 44 millimeters long. Females are a bit bigger, measuring 52 to 62 millimeters from snout to vent. These frogs have bright red eyes with pupils that look like thin lines. Their backs are usually a light or dark leaf green color. The sides of their bodies are a pretty bluish-purple. They also have large suction cups on their fingers and toes. These cups help them stick to surfaces. They also have lots of skin between their fingers and toes, like webbing.
Where They Live and What They Do
Agalychnis saltator frogs are nocturnal, which means they are active at night. They are also arboreal, meaning they live in trees. Their favorite homes are humid and wet forests in lowlands and mountains. You might also find them in nearby rainforests.
These frogs usually stay high up in the tree canopies. But when it's time to have babies, they come down to temporary pools of water. Male frogs can jump from very high places to plants near these mating pools. They spread out their limbs and the webbed skin between their fingers and toes. This helps them glide down, almost like a parachute! That's why they are called "parachuting frogs."
Life Cycle and Reproduction
Agalychnis saltator frogs are "explosive breeders." This means they all come together to have babies after heavy rains. A single group of breeding frogs can have anywhere from 25 to 400 frogs. Most often, you'll see about 100 to 200 frogs in one group.
They gather on vines that hang over temporary ponds in the forest. They also use marsh plants like Spathiphyllum. In these groups, many frogs are paired up. Sometimes, one female frog might have one to four male frogs with her. They lay their eggs among the moss that covers the vines. However, these eggs can be easily eaten by other animals at this stage.
Sometimes, male Agalychnis saltator frogs have been seen trying to mate with females of another frog species, Agalychnis callidryas. But any eggs from these pairings cannot develop into baby frogs.
Protecting the Parachuting Red-Eyed Leaf Frog
The Agalychnis saltator naturally lives in separate areas. It's not a very common frog, but you can usually find it at its breeding sites. Sadly, its home is becoming even more broken up. This is happening because of deforestation for farms and logging.
Even though its habitat is shrinking in some places, the frog is not considered threatened overall. However, these frogs are sometimes caught and sold illegally as pets. Because of this, the Agalychnis saltator is listed in CITES Appendix II. This means there are rules to control its trade and protect it.


