Frog facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Frog |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Northern leopard frog (Lithobates pipiens) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: |
Anura
Merrem, 1820
|
 |
|
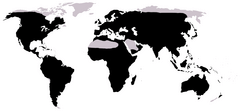
| Distribution of frogs (in black) | |
Frogs are amazing amphibians. This means they can live both on land and in water. They belong to a group called Anura. There isn't much difference between frogs and toads. Toads usually have drier, rougher skin, which helps them live in drier places. This "toad look" has evolved many times in different frog groups.
Frogs can live on land and in fresh water, but they can't survive in salty water. They grow through a process called metamorphosis. It usually starts when a female frog lays eggs, which are often called frogspawn. These eggs hatch into tadpoles. Tadpoles have tails and gills, which help them breathe underwater.
The next stage is a "froglet." Froglets develop lungs to breathe air, but they still have tails. Finally, a fully grown frog has long legs and no tail. Adult frogs use their strong legs to jump. They also have long, sticky tongues to catch bugs. Frogs are known for the sounds they make, called croaks. Some species of frogs live in trees, and some are poisonous to protect themselves from animals that might want to eat them. Frogs live all over the world. If a new type of frog is brought into an area, it can sometimes change the local ecosystem.
Sometimes, frog legs are eaten as food in places like France, China, and parts of the United States. If too many frogs are removed from an area, it can affect the ecosystem. For example, frogs eat mosquitoes. If there are fewer frogs, there might be more mosquitoes, which can lead to more diseases that mosquitoes carry. Frogs are part of the class Lissamphibia, which is the only group of amphibians still alive today.
Contents
Frog Characteristics
Frogs are cold-blooded animals. This means their body temperature changes with the temperature around them. They need warmth to stay active. Amphibians get heat from the sun, but usually not directly, because too much sun can dry out their skin. Some frogs aestivate (like hibernating) during winter or dry times. They often hide underground in mud or holes. They can breathe oxygen through their skin while they are aestivating. They come out when the weather is good again.
The shape of a frog's feet and legs depends on where it lives. Some live on the ground, some in water, some in trees, and some in burrows. Frogs need to move fast to catch food and escape danger. Most frogs are excellent jumpers, or they come from ancestors who were.
Each frog species has its own special call or croak. Frogs make this sound by pushing air through their voice box, called the larynx. Many frogs have vocal sacs that make their calls even louder. Some frog calls can be heard up to a mile away! The main reason male frogs call is to attract a mate.

Frogs have smooth skin with no scales or hair. They can take in oxygen from both water and air through their skin. Their skin also produces mucus to keep it wet and slippery. Many amphibians have toxic skin, meaning it can be poisonous if touched or eaten by other animals.
Many frogs are semi-aquatic, meaning they live both on land and in water. They prefer damp places like ponds, swamps, rivers, and lakes. Most adult frogs stay near where they grew up. Many amphibians lay their eggs in foam nests. Frogs can hear sounds both in the air and underwater.
Camouflage is a common way frogs protect themselves. Most camouflaged frogs are active at night. During the day, they find a spot where they can blend in with their surroundings and stay hidden.
Frog Life Cycle: Metamorphosis
At the end of the tadpole stage, a frog goes through a quick change called metamorphosis. Its body suddenly transforms into the adult form. This change usually happens in just 24 hours and is started by a hormone called thyroxine. This hormone makes different parts of the tadpole's body develop in new ways.
During metamorphosis, the tadpole's gills and gill pouch disappear, and its lungs grow so it can breathe air. Its front legs also become visible. The tadpole's lower jaw changes into the larger jaw of an adult frog, which eats meat. The long, coiled gut of the plant-eating tadpole becomes the short gut of a predator. The frog's nervous system also changes to improve its hearing and vision, and to help it move and eat in new ways.
The eyes move higher on the head, and eyelids develop. The eardrum and inner ear also form. The skin becomes thicker and tougher, and skin glands develop. The last part of the change is when the tail disappears. The body uses the tail's tissue to help the legs grow quickly. Frogs are most at risk from predators during metamorphosis because they are losing their tail and are just learning to move with their new legs.
Variations in Frog Development
Most frogs develop from tadpoles that hatch from eggs laid in water. Usually, the eggs are fertilized outside the female's body after they are laid. However, some frogs have internal fertilization, meaning the eggs are fertilized inside the female before she lays them.
A new species was found in Sulawesi, Indonesia, that gives birth to live tadpoles! This frog is called Limnonectes larvaepartus.
The Limnonectes family of frogs are known as 'fanged frogs' because they have two small bumps on their lower jaws that look like fangs and are used in fighting. This special frog lives in the tropical rainforests of Sulawesi, an island that is sadly losing its forests quickly.
- The biggest frog in the world is the African Goliath frog (Conraua goliath). It can weigh up to 3.8 kilograms (8.4 pounds) and be 39 centimeters (15 inches) long from its snout to its rear.
- Paedophryne amauensis is the smallest frog, and also the smallest vertebrate (animal with a backbone). It is only 7.7 millimeters (0.30 inches) long!
Where Frogs Live: Distribution and Habitats
Frogs live all over the world and have learned to survive in many different climates, even deserts. They have special adaptations that help them. For example, frogs of the Cyclorana group live in the central Australian desert. They bury themselves underground and create a waterproof cocoon to stay safe during dry times. When it rains, they come out, find a temporary pool, and quickly lay their eggs and breed. Their eggs and tadpoles develop very fast so they can finish growing before the pond dries up again.
Some frog species can even live in very cold places. The wood frog (Rana sylvatica) lives in areas that reach into the Arctic Circle. It buries itself in the ground during winter. Even though much of its body freezes, it has a lot of glucose (a type of sugar) in its important organs, which protects them from damage.
There are also many tiny tree frogs that lay their eggs in water pools found on tropical leaves, high up in trees. Most of these frogs only come down to the ground to mate. Tree frogs have evolved many times, but they all have very similar ways of living and looking. This is an example of convergent evolution, where different species develop similar traits because they live in similar environments.
Overall, frogs are a very successful and widespread group of animals. There are about 4,800 known species, which is more than 85% of all living amphibian species. They are one of the five most diverse groups of animals with backbones.
Uses of Frogs
Frog legs are eaten by people in many parts of the world. In France, "cuisses de grenouille" (frog legs) is a traditional dish. It's also popular in French-speaking parts of Louisiana, especially in Cajun areas and New Orleans in the United States. In Asia, frog legs are eaten in China, Vietnam, Thailand, and Indonesia.
The Chinese edible frog and pig frogs are raised on farms and eaten a lot in some parts of China. Frog legs are part of Chinese Sichuan and Cantonese cuisine. In Indonesia, frog-leg soup is called swikee. Indonesia is the biggest exporter of frog meat in the world, sending over 5,000 tons of frog meat each year, mostly to France, Belgium, and Luxembourg.
At first, frogs were caught from the wild, but too much hunting led to fewer frogs. This led to frog farming and a global trade in frogs. The main countries that buy frog meat are France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and the United States. The main countries that sell frog meat are Indonesia and China. The trade of the American bullfrog, mostly raised in China, is about 1,200 to 2,400 tons each year.
The mountain chicken frog is called that because it tastes like chicken. This frog is now endangered, partly because people eat it. It used to be a very popular food choice for people in Dominica.
Images for kids
-
Variegated golden frog (Mantella baroni) in the Ranomafana National Park of Madagascar
-
European fire-bellied toad (Bombina bombina)
-
Panamanian golden frog (Atelopus zeteki).
-
A fossilized frog from the Czech Republic, possibly Palaeobatrachus gigas.
-
A bullfrog skeleton, showing elongated limb bones and extra joints. Red marks indicate bones which have been substantially elongated in frogs and joints which have become mobile. Blue indicates joints and bones which have not been modified or only somewhat elongated.
-
Webbed hind foot of common frog (Rana temporaria)
-
Northern leopard frog (Rana pipiens) moulting and eating its skin.
-
Rainforest rocket frog jumping.
-
Common toad (Bufo bufo) swimming.
-
Group of glass frogs
-
Male and female common toads (Bufo bufo) in amplexus.
-
Pouched frog (Assa darlingtoni)
-
The mildly toxic Ranitomeya imitator.
-
Strawberry poison-dart frog contains numerous alkaloids which deter predators.
-
Although frogs are most diverse in warm regions, a few species like the wood frog even live at the Arctic Circle
-
Golden toad (Bufo periglenes) – last seen in 1989.
-
Deformed mink frog with an extra left leg
-
Golden poison frog (Phyllobates terribilis).
-
Moche frog sculpture
-
Wood Frog (Lithobates sylvaticus or Rana sylvatica) uses disruptive coloration including black eye markings similar to voids between leaves, bands of the dorsal skin (dorsolateral dermal plica) similar to a leaf midrib as well as stains, spots & leg stripes similar to fallen leaf features.
-
Pouched frog (Assa darlingtoni) camouflaged against leaf litter.
See also
 In Spanish: Anuros para niños
In Spanish: Anuros para niños