Anglo-Persian capture of Hormuz facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Capture of Hormuz |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
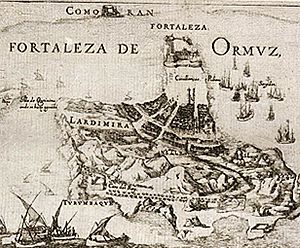
 The taking of Hormuz by Imam Quli Khan and his army (Latin inscription round the fortress). From a Jarūnnāmeh by Qadrī. Isfahan style, dated 1697. |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||||
| Strength | |||||||||
| 3,000 5 warships 4 pinnaces |
1,000 | ||||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||||
| Light | Light 1,000 captured |
||||||||
The Capture of Hormuz (in Persian: بازپس گیری هرمز) was a big event in 1622. It was a joint effort by the Persian army and the English navy. They worked together to take over Hormuz Island from the Portuguese.
This victory happened after a ten-week long attack, called a siege. It helped Persia open up new trade routes with England in the Persian Gulf. Before this, the Portuguese had controlled the Castle of Hormuz for over 100 years. They had captured it in 1507. This gave them full control over trade between India and Europe through the Persian Gulf. The capture of Hormuz completely changed who had power and control over trade in the region.
Contents
Working Together: The Anglo-Persian Alliance
The English part of this alliance came from the East India Company. They provided five warships and four smaller ships called pinnaces. At this time, the Persians were already fighting the Portuguese. A Persian army was trying to capture a Portuguese fort on Kishm Island. But they needed help from the English to take Hormuz.
Shah Abbas, the ruler of Persia, wanted English support against the Portuguese. His commander, Imam Quli Khan, talked with the English. He promised them that if they helped, they would get access to the valuable Persian silk trade.
They signed an agreement. This agreement said they would share anything they captured. They would also share the money collected from customs (taxes on goods) at Hormuz. Prisoners would be sent back to their home countries based on their religion. Finally, the Persians agreed to pay half of the costs for the English fleet.
How the Battle Unfolded
The English fleet first sailed to Qeshm, which is about 24 kilometers away. There, they attacked a Portuguese position with their cannons. The Portuguese soldiers quickly gave up. The English had very few injuries, but sadly, the famous explorer William Baffin was among them. He later died from his wounds.
After Qeshm, the combined English and Persian fleet sailed to Hormuz Island. The Persian soldiers got off their ships to capture the town. Meanwhile, the English ships fired their cannons at the Portuguese castle. They also sank the Portuguese ships in the harbor.
After some fighting, the Portuguese finally surrendered Hormuz on May 4, 1622. The Portuguese forces had to leave and move to another base in Maskat.
At the time, Portugal and Spain were ruled by the same king (this was called a dynastic union from 1580 to 1640). Even though England and Portugal were not officially at war, the Duke of Buckingham was upset. He threatened to sue the East India Company for capturing Hormuz. But he dropped his claim when he received 10,000 pounds. This was supposedly 10% of the money made from the capture of Hormuz. King James I also received the same amount from the company. He had complained, saying, "Did I deliver you from the complaint of the Spaniards, and do you return me nothing?"

The capture of Hormuz gave the East India Company a chance to trade more with Persia. They tried to sell English cloth and other goods in exchange for silk. However, this trade did not become very profitable. This was because Persians were not very interested in English goods, and the English did not have many goods to offer. The English soldier and merchant Robert Shirley was also very interested in making this Anglo-Persian trade stronger.
See also
Images for kids
 | Roy Wilkins |
 | John Lewis |
 | Linda Carol Brown |