Anne Rudge facts for kids
Anne Rudge (born October 29, 1761 – died September 1, 1836) was a talented British artist. She was known for her detailed botanical illustrations. She drew plants for books by her husband, Edward Rudge, and her son, Edward John Rudge. Anne was one of the first female botanical artists to sign her work. This was unusual for women artists at that time.
Contents
Anne Rudge's Early Life
Anne Nouaille was born in London in 1761. Her parents were Elizabeth and Peter Nouaille. Her family came from France. They were Huguenots, who were Protestants who had to leave France. Her father, Peter, was a silk maker. He was also a Justice of the Peace in Sevenoaks, Kent.
Anne received an excellent education. Her father made sure she learned many things. She became good at modern and ancient languages. She also excelled in music and art. She married the botanist and antiquary Edward Rudge in London on July 28, 1791. They had three children: Edward John, Anne Eliza, and Samuel Nouaille.
Becoming a Botanical Illustrator
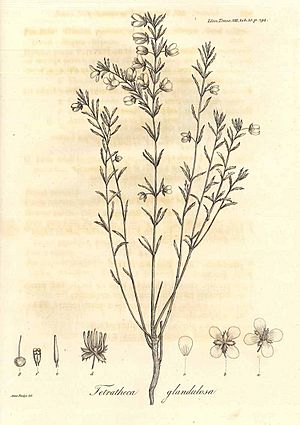
Anne Rudge started making prints around 1799. She often put plate numbers on her prints. Her husband, Edward, taught her how to draw plants very accurately. She became skilled at making precise and detailed botanical illustrations.
Illustrating Plants for Science
Anne drew fifty plates for her husband's book, Plantarum Guianæ rariorum icones et descriptiones hactenus ineditæ (1805–07). She also drew pictures for his scientific papers. These papers were for the Linnean Society. Anne understood how plants were classified. Her drawings showed the tiny details needed by plant scientists. This included the parts of plants used for reproduction.
Her work was so well-known in the plant world that a type of water lily was named after her. This was a great honor.
Anne's Artistic Skills
Anne was already good at drawing landscapes and nature before she married. Her husband helped her improve her skills for scientific illustration. Her drawings were large, clear, and very precise. She simplified plants in her art. This helped make complex details easier to understand for botanists.
After Anne died in 1836, her husband wrote about her. He said her father helped her develop her natural talents. She learned many languages, including French, Italian, Spanish, and Latin. She even studied Hebrew to read the Bible.
Her husband also wrote that Anne was an excellent musician. She could play difficult music easily. She loved playing music by famous composers like Handel.
Her drawing and etching skills were just as good. She copied nature faithfully and precisely. She drew both landscapes and natural history. Her knowledge of botany, learned from her husband, helped her illustrate his works. She drew new plant species from New Holland (now Australia). She also illustrated his book on plants from Guiana. Her drawings showed the tiny, magnified parts of flowers with great accuracy. This helped her understand how flowers are formed.
Her botanical work was recognized in other countries. A water lily species was named after her. This was a compliment to her excellent drawings. She was compared to other famous female botanists and illustrators.
Anne also illustrated her husband's and eldest son's works. These were for the Society of Antiquaries. She drew ancient discoveries from Evesham Abbey.
Later Life and Legacy
Anne Rudge passed away in 1836 after a short illness. She was buried in the Rudge family tomb. This was at St Lawrence's church in Evesham. On the day of her funeral, local businesses closed. This showed how much people respected her. Her husband was later buried with her.



