Anterograde amnesia facts for kids
Anterograde amnesia is a type of amnesia, which means having trouble remembering things. When someone has anterograde amnesia, they find it hard to form new memories after a specific event. It's like their brain can't save new information into long-term storage. However, they can usually still remember things that happened before that event. This memory problem can be mild or very severe.
Contents
What is Anterograde Amnesia?
Anterograde amnesia means that after a certain point in time, a person struggles to create new memories. Imagine reading a book, and every time you turn the page, you forget what happened on the previous one. People with this condition might meet someone new and then forget their name a few minutes later. They might also forget recent conversations or events.
This is different from forgetting things that happened a long time ago. Their older memories, from before the amnesia started, are usually still clear. The problem is with making new memories stick.
Anterograde vs. Retrograde Amnesia
Sometimes, anterograde amnesia happens along with another type called retrograde amnesia.
- Anterograde amnesia means you can't form new memories after an event.
- Retrograde amnesia means you can't remember things that happened before an event.
For example, after a concussion (a type of brain injury), a person might have both. They might not remember the accident itself (retrograde) and also struggle to remember things that happen in the hours or days right after the accident (anterograde).
What Causes Anterograde Amnesia?
Anterograde amnesia can be caused by different things that affect the brain's ability to form new memories.
- Certain Medicines: Some types of medicine, like certain sedatives (for example, Benzodiazepines), can temporarily stop the brain from making new memories while the medicine is active.
- Brain Injuries: Serious head injuries, also known as traumatic brain injury, are a common cause. These injuries can damage parts of the brain important for memory.
- Diseases: Certain illnesses that affect the brain can also lead to anterograde amnesia. This happens when the disease damages the areas of the brain responsible for memory.
How the Brain Makes Memories
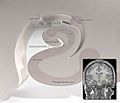
Our brain has special parts that help us remember things. One very important part is called the Hippocampus. It's located deep inside the brain and acts like a memory "save button." When we learn something new, the hippocampus helps move that information from short-term memory (like remembering a phone number for a few seconds) into long-term memory (like remembering your best friend's name). If the hippocampus is damaged, it becomes very hard to save new memories.
Living with Anterograde Amnesia
Living with anterograde amnesia can be challenging. People might need help remembering daily tasks or appointments. They might use notes, alarms, or have family members help them. Even though they can't form new memories, they can often still learn new skills, like playing a musical instrument, even if they don't remember learning it! This shows that different parts of the brain handle different types of memory.
Images for kids
See also