Concussion facts for kids
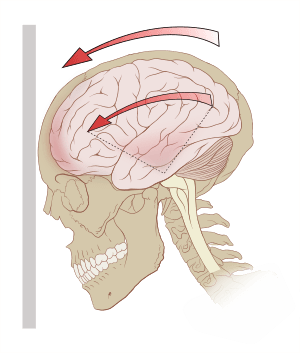
A concussion is a common type of brain injury that happens when your head gets a bump, blow, or jolt. It can also happen if your body is hit hard and your head moves quickly back and forth. This quick movement makes your brain shake inside your skull. Even though it's called a "mild traumatic brain injury," a concussion is still serious. It causes a temporary change in how your brain works.
You might not even realize you have a concussion because the signs can be subtle. Common causes include sports injuries, bike accidents, car accidents, and falls. For kids, sports are a big reason for concussions. Less than 10% of sports-related concussions in children involve losing consciousness.
It's not fully clear exactly what damage happens inside the brain or how all the symptoms are caused. However, we know that tiny parts of brain cells, called axons, can stretch. Also, small changes happen in the brain's ion channels, which are like tiny gates on cells.
The main treatment for a concussion is rest. This means both physical rest (like not playing sports) and mental rest (like taking a break from schoolwork, video games, and texting). Most symptoms usually get better within a few weeks.
Concussions are quite common, affecting more than 6 out of every 1,000 people. If you've had one concussion, you might be more likely to get another, especially if the new injury happens before you've fully recovered from the first one. Getting repeated concussions can increase the risk of problems later in life, like memory issues or feeling down.
Contents
What are the Signs of a Concussion?
Concussion symptoms usually show up quickly after the injury. How many symptoms you have and what kind they are can be very different for each person. Most early symptoms get better within days or weeks.
Physical Symptoms
A Headache is the most common symptom after a concussion. Other physical signs can include feeling dizzy, sick to your stomach, or even throwing up. You might also have trouble with your balance or feel clumsy.
Your vision can also be affected. You might be sensitive to bright light (called photophobia), see blurry, or even see double (called diplopia). Some people also hear ringing in their ears, which is called Tinnitus.
Sometimes, a concussion can cause a brief convulsion. These are usually not serious and don't mean you'll have post-traumatic epilepsy later on. They are just a temporary reaction of the brain.
Thinking and Feeling Changes
Concussions can make you feel confused or disoriented. It might be hard to focus your attention. You might lose consciousness, but even a brief loss of consciousness doesn't always mean the concussion is more severe.
A common sign is Post-traumatic amnesia, where you can't remember what happened right after the injury. You might also feel confused, repeat the same questions, or be slow to answer. Your speech might seem slurred. Other symptoms include changes in how you sleep and difficulty with thinking clearly or doing everyday tasks.
Concussions can also change your mood. You might feel cranky, lose interest in things you usually enjoy, or cry easily. Kids with concussions often seem restless, tired, or irritable.
How Does a Concussion Happen?

Your brain is protected by a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid, which acts like a cushion. But if the impact is too strong, or if your head moves very quickly, this cushion might not be enough.
A concussion can happen from a direct hit to the head, like when your head strikes something. It can also happen from "impulsive forces," where your head moves suddenly without a direct hit, like when your body stops quickly and your head snaps forward.
When your head moves, your brain can move in different ways: straight, rotating (spinning around its center), or angular (spinning around an axis not through its center). Experts believe that the amount of rotational force is a major factor in how severe a concussion is.
After a concussion, the forces from the injury can temporarily disrupt the normal activities of your brain cells. This can affect how your brain works and cause symptoms like losing consciousness.
When to See a Doctor: Red Flags
It's very important to check for more serious problems after a head injury, like bleeding inside the brain. Doctors will check your breathing and circulation. If an athlete is unconscious after a head or neck injury, doctors will also check their neck very carefully.
| Red flag |
|---|
| Seizure |
| Worsening headache |
| Difficulty waking up |
| Seeing double |
| Problem recognizing people or places |
| Repeated vomiting |
| New weakness or numbness |
| Not acting like themselves |
You should get immediate medical help if you see any of these "red flags":
- A Seizure
- A headache that gets worse
- Trouble waking up
- Seeing double
- Trouble recognizing people or places
- Throwing up many times
- New weakness or numbness in arms or legs
- Not acting like their usual self
If someone has these symptoms, or if doctors are worried about a more serious brain injury, they might do a brain scan to look for problems. They might also watch the person closely for 24 to 48 hours.
Doctors diagnose a concussion based on a physical exam and how the person is acting. They also look at how long someone was unconscious (usually less than 30 minutes) and how long they had Post-traumatic amnesia (usually less than 24 hours). There are also special Neuropsychological tests that measure how well your brain is thinking.
Sometimes, concussions are not diagnosed because the signs aren't obvious, or athletes might try to hide their injury to keep playing.
How to Prevent Concussions
You can take steps to prevent concussions:
- Always wear seat belts in cars and make sure airbags are working.
- For older people, it's good to keep floors clear of clutter and wear flat, thin shoes to help with balance and prevent falls.
For athletes, protective gear like helmets can help reduce concussions. Newer helmet designs are always being developed to make them safer. Some helmets even have technology to study impacts, which helps us learn more about how concussions happen in sports like American Football.
Changing rules in sports or making sure existing rules are followed can also help. For example, rules against "head-down tackling" in football can prevent many injuries.
How to Treat a Concussion
After a head injury, doctors will observe the person for several hours. If serious symptoms like repeated vomiting, worsening headache, or seizures appear, it's important to go to an emergency room right away.
The most important treatment for a concussion is physical and cognitive rest. This means resting your body and your brain until all your symptoms are gone. Most concussions (80-90%) get better in about 7 to 10 days, but it can take longer for children and teenagers.
Cognitive rest means reducing activities that make your brain work hard. This includes:
- Schoolwork
- Playing video games
- Text messaging
- Even reading for fun can sometimes make symptoms worse for kids.
It's often suggested that students take time off from school or attend for only part of the day. Since students might look fine, it's important for teachers and school staff to understand concussions.
Rest also means getting enough sleep at night and resting during the day. You should slowly go back to your normal activities only when they don't make your symptoms worse. Learning about your symptoms and how to manage them can help you recover better.
For athletes, there are clear steps to follow before returning to play. You should be completely free of symptoms before starting any activity. Then, you gradually increase your activity level:
- Complete physical and mental rest.
- Light aerobic activity (like walking or light cycling).
- Sport-specific activities (like running drills).
- Non-contact training (like practice drills without hitting others).
- Full-contact practice.
- Full-contact games.
You should only move to the next step if you've been symptom-free for 24 hours. If symptoms come back, you must go back to the previous step where you had no symptoms and stay there for at least another 24 hours. The main goal is to stay symptom-free and take it slow.
What Happens After a Concussion?
If you've had one concussion, you might be more likely to get another one. This is especially true if the new injury happens before you've fully recovered from the first one. Also, sometimes smaller impacts can cause the same severe symptoms if you've had previous concussions.
Getting repeated concussions can increase the risk of problems later in life, such as memory issues or feeling down.
Images for kids
-
Guillaume Dupuytren, a French surgeon, helped us understand the difference between a concussion and other brain injuries.
See also
 In Spanish: Conmoción cerebral para niños
In Spanish: Conmoción cerebral para niños