Austenite facts for kids
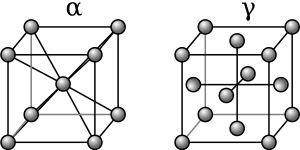
Austenite is a special metallic form of iron. Think of it like iron that has changed its internal structure. It's one of the different ways iron can exist, called an allotrope. This means it's still chemically iron, but its physical arrangement of atoms is different. Austenite is named after Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen, a famous metallurgist who lived from 1843 to 1902.
What is Austenitization?
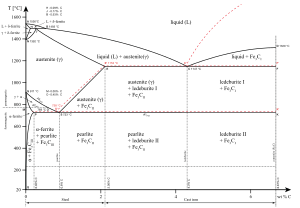
Austenitization is a process where we heat iron, steel, or other iron-based metals to a very high temperature. When these metals get hot enough, their internal structure changes.
How Metal Changes
At this high temperature, the metal's crystal structure transforms. It changes from a form called ferrite into austenite. This new austenite structure is special because it can absorb and hold more carbon. Carbon is a key ingredient in making steel stronger.
Two-Phase Austenitization
Sometimes, when certain types of iron or steel are heated, tiny particles called carbides might also be present. When this happens during the heating process, it's often called two-phase austenitization. This means two different types of structures are present at the same time.
See also
 In Spanish: Austenita para niños
In Spanish: Austenita para niños