Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM)
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Former autonomous region of the Philippines | |||||||||||
| 1989–2019 | |||||||||||
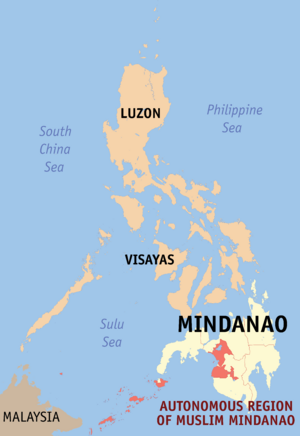 Location within the Philippines |
|||||||||||
| Capital | Cotabato City (provisional and de facto seat of government) Parang (de jure seat of government, 1995–2001) |
||||||||||
| Population | |||||||||||
|
• 2015
|
3,781,387 | ||||||||||
| History | |||||||||||
|
• Established
|
1 August 1989 | ||||||||||
|
• Turnover of ARMM to BARMM
|
26 February 2019 | ||||||||||
| Political subdivisions | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Today part of | Bangsamoro Autonomous Region | ||||||||||
The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) was a special area in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines. It was an autonomous region, which means it had its own government. This was different from other regions in the Philippines.
ARMM was made up of five provinces: Basilan (but not Isabela City), Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi. The region was created in 1989 and lasted until 2019. It was then replaced by a new region called Bangsamoro.
Images for kids
-
Daru Jambangan (Palace of Flowers) in Maimbung, Sulu before it was destroyed by a typhoon in 1932.
-
Tausūg horsemen in Sulu, taken on December 30, 1899.
-
Pastil, a traditional Maguindanaon food.
See also
 In Spanish: Mindanao Musulmán para niños
In Spanish: Mindanao Musulmán para niños

All content from Kiddle encyclopedia articles (including the article images and facts) can be freely used under Attribution-ShareAlike license, unless stated otherwise. Cite this article:
Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao Facts for Kids. Kiddle Encyclopedia.






















