Atmospheric pressure facts for kids
Atmospheric pressure is the force that the weight of air pushes against a surface. Think of it as the weight of all the air above you. Our Earth is surrounded by a thick layer of air called the atmosphere. This air has weight, and it presses down on everything.
The amount of air pressing down changes from place to place. When there is more air above a spot, the pressure is higher. When there is less air, the pressure is lower. This is why atmospheric pressure is always changing.
Contents
What is Atmospheric Pressure?
Air might seem light, but it actually has weight. Imagine a tall column of air stretching from the sky all the way down to the ground. The weight of all that air in the column creates atmospheric pressure. This pressure pushes on everything around us, from all directions. We don't usually feel it because our bodies are also filled with air, pushing back.
How Altitude Affects Pressure
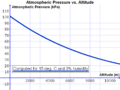
The higher you go, the less air there is above you. This means there is less weight pushing down. So, the higher you are, the lower the atmospheric pressure. For example, if you climb a tall mountain, the air will be "thinner." This is why some people find it harder to breathe at very high altitudes. There isn't as much air pushing into their lungs.
How Weather Affects Pressure
Atmospheric pressure also changes with the weather.
- High pressure usually means clear, sunny skies. This is because a lot of heavy, cool air is sinking.
- Low pressure often brings cloudy, stormy weather. This happens when lighter, warm air rises. Weather forecasters use these changes to predict if it will rain or be sunny.
Measuring Atmospheric Pressure
Scientists use a tool called a Barometer to measure atmospheric pressure. Barometers help us understand changes in the weather.
Units of Measurement
The standard unit for atmospheric pressure is the hectopascal (hPa). You might also see it measured in millibars (mbar). These units help scientists and weather experts compare pressure readings from different places.
Images for kids
-
A very local storm above Snæfellsjökull (Iceland), showing clouds formed on the mountain by orographic lift
-
Hurricane Wilma on 19 October 2005; 882 hPa (12.79 psi) in the storm's eye
See also
 In Spanish: Presión atmosférica para niños
In Spanish: Presión atmosférica para niños