Basal ganglia facts for kids
The basal ganglia are super important parts deep inside your brain. Think of them as control centers! They are found under the main wrinkly part of your brain, called the cerebral cortex. These special areas are connected to other brain parts, like the midbrain and the thalamus. They are super important for how you move. If they get damaged, it can be hard to move properly.
These brain areas work together to help you do many things. They help you control your eye movements. They also help with actions you choose to do, like picking up a pencil. Plus, they help you learn habits, like riding a bike or tying your shoes without thinking too much. They even play a role in how you feel and make decisions.
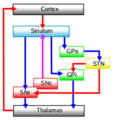
The basal ganglia also help with your motivation. They help you choose what to do at any moment. Imagine your brain has many ideas for actions. The basal ganglia help to "turn off" or stop some of these ideas. Then, they "turn on" the one action you want to do. This "switching" between behaviors is guided by signals from many parts of your brain. One key part is the prefrontal cortex, which helps you plan and decide things.
Contents
How Your Brain Controls Movement
The basal ganglia are like a traffic controller for your movements. They make sure your body does the right actions at the right time. They stop unwanted movements and allow the movements you want to make. This helps you move smoothly and purposefully.
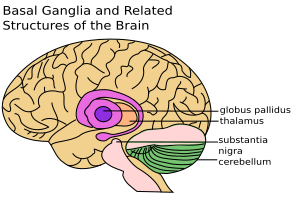
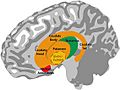
Parts of the Basal Ganglia
The basal ganglia are made up of several important parts. These parts work together like a team:
- Striatum: This is a big part that includes:
- The caudate nucleus
- The putamen
- Pallidum (also called globus pallidus): This part helps control movement. It includes:
- The substantia nigra
- The nucleus accumbens
- Subthalamic nucleus: This small part also helps control movement.
Basal Ganglia Through Time
The basal ganglia are very old parts of the brain. They can be found in almost all animals with a backbone, called vertebrates. Even in very simple animals like the lamprey (a type of fish), we can see similar parts. This shows how important these brain areas are for basic life functions.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ganglios basales para niños
In Spanish: Ganglios basales para niños
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |