Cerebral cortex facts for kids
The cerebral cortex is a very important part of your brain. It's like the brain's main control center! In humans, it's the biggest part of the brain.
Even though you can't see it directly, different areas of the cerebral cortex have special jobs. It helps you with things like memory, paying attention, understanding what you see and hear, thought, language, and even being aware of yourself and the world around you.
The cerebral cortex is a thin layer of brain tissue on the outside of the cerebrum. Think of it like a thin blanket covering the top of your brain. It's made up of many nerve cells arranged in layers, usually up to six. In humans, this layer is about 2 to 4 millimeters thick. That's about the thickness of a few credit cards stacked together!
When scientists look at preserved brains, the cerebral cortex appears grey. That's why it's often called 'grey matter'. This grey matter is full of nerve cells. Below it, there's 'white matter', which is mostly made of axons. These are like tiny wires that connect nerve cells in different parts of the brain and to other parts of your central nervous system.
In large mammals like humans, the surface of the cerebral cortex is folded. This means it has lots of bumps and grooves. These folds allow more of the cerebral cortex to fit inside your skull. In fact, more than two-thirds of the human cerebral cortex is hidden within these grooves!
Neocortex: The Newest Part
The neocortex is the newest part of the cerebral cortex to have evolved. It's the most advanced part and has six layers of nerve cells. This six-layer neocortex is a special feature of mammals. It's found in the brains of all mammals, but not in other animals. In humans, about 90% of our cerebral cortex is neocortex.
The neocortex is where many of our higher-level thinking skills happen. This includes things like problem-solving, planning, and understanding complex ideas.
How Your Brain Works
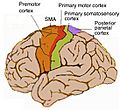
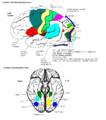
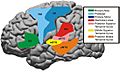
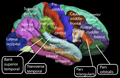
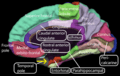
Different areas of the cerebral cortex are responsible for different functions. For example:
- The motor cortex helps you control your body's movements.
- The sensory cortex helps you feel touch, temperature, and pain.
- The visual cortex processes what you see.
- The auditory cortex processes what you hear.
- Areas like the frontal lobe are involved in decision-making, personality, and planning.
These different parts work together, forming complex networks that allow you to do everything you do, from reading this sentence to playing sports or creating art.
Images for kids
-
Micrograph showing the visual cortex (predominantly pink). Subcortical white matter (predominantly blue) is seen at the bottom of the image. HE-LFB stain.
-
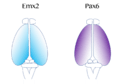
Depicted in blue, Emx2 is highly expressed at the caudomedial pole and dissipates outward. Pax6 expression is represented in purple and is highly expressed at the rostral lateral pole. (Adapted from Sanes, D., Reh, T., & Harris, W. (2012). Development of the Nervous System (3rd ed.). Burlington: Elsevier Science)
-
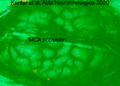
Hemodynamic changes observed on gyrencephalic brain cortex after an arterial vessel occlusion in IOS. The video has a speed of 50x to better appreciate the spreading depolarization over the brain cortex. Pictures are dynamically subtracted to a reference picture 40 s before. First we see the initial are of change at the exact moment where the middle cerebral artery group (left) is occluded. The area is highlighted with a white line. Later we appreciate the signal produced by Spreading Depolarizations. We see markedly the front of waves. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04132-8
See also
 In Spanish: Corteza cerebral para niños
In Spanish: Corteza cerebral para niños