Black birch facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Black birch |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| The bark of a young river birch | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fagales |
| Family: | Betulaceae |
| Genus: | Betula |
| Subgenus: | Betula subg. Neurobetula |
| Species: |
B. nigra
|
| Binomial name | |
| Betula nigra |
|
 |
|
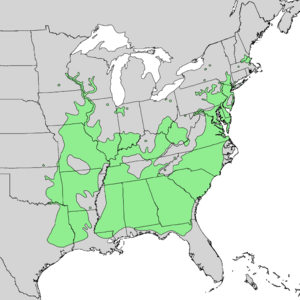
| Natural range of Betula nigra | |
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The River Birch, also known as black birch or water birch, is a type of birch tree. It grows naturally in the eastern parts of the United States. You can find it from New Hampshire all the way down to northern Florida, and west to Texas. Unlike many birches that like cold weather, the River Birch can handle warmer temperatures. It often grows in wet places like floodplains (areas near rivers that flood) and swamps.
Contents
What Does a River Birch Look Like?
The River Birch is a deciduous tree, meaning it loses its leaves in the fall. It can grow very tall, up to about 80 to 100 feet (25-30 meters). Its trunk can be quite wide, from about 20 to 60 inches (50-150 cm) across. Often, the bottom of the tree splits into several thinner trunks.
Its Unique Bark
The bark of a River Birch changes as the tree gets older.
- Young trees: The bark is often a salmon-pink or brown-gray color. It peels off in loose, paper-thin layers that curl up.
- Mature trees: The bark turns a reddish-brown color with a dark gray base. The peeling layers are thicker and pressed flat against the trunk. They might stick out a little on the sides.
- Old trees: The bark at the bottom of the trunk becomes very thick. It has deep cracks and furrows.
Leaves and Flowers
The small branches, called twigs, are usually smooth or slightly hairy. River Birch leaves are oval-shaped. They are about 1.5 to 3 inches (4-8 cm) long and 1 to 2.5 inches (3-6 cm) wide. The edges of the leaves are jagged, like a saw. The top of the leaf is dark green, and the underside is a lighter yellow-green. In autumn, the leaves turn a bright yellow color.
The tree's flowers are called catkins. They are long, hanging clusters about 1 to 2.5 inches (3-6 cm) long. The male catkins hang down, while the female catkins stand upright. The wind carries pollen from the male to the female catkins. The fruit of the River Birch is special because it ripens in late spring. It contains many tiny seeds with wings, packed between the catkin parts.
Where Does the River Birch Grow?
You can often find the River Birch in lower areas. It grows from Massachusetts in the north down to northern Florida. It also stretches west to Kansas and east to the coast. As its name suggests, it loves to grow along the sides of streams and rivers. It's also common in wet forests and places with moist soil, like floodplains.
This tree grows in many states, including Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Maryland, New York, North Carolina, and Texas. It does best in plant hardiness zones 4-9, which means it can handle a good range of temperatures.
Conservation Status
In the state of New Hampshire, the River Birch is considered a threatened species. This means its population is at risk.
How River Birches Help Nature
River Birches are very useful, especially in areas where mining has happened. They are often planted to help fix the land and stop soil from washing away. This is because they can grow well in acidic soils that other trees might not like.
Since these trees grow mostly in floodplains and along riverbanks, they can handle being flooded for a while. Young trees have been seen to survive up to 30 days of continuous flooding! However, River Birches need a lot of sunlight. Their seeds won't sprout if there isn't enough direct sun.
How New Trees Grow
River Birches usually produce seeds every year. Male catkins start to form in the fall. Female catkins appear in early spring, around the same time the leaves return. Both male and female fruits are ready in late spring or early summer.
Once the seeds are ready, they are mostly spread by wind or by water from nearby streams. Seeds carried by water are often more successful. This is because the moist banks of stream channels are perfect for the seeds to sprout and grow strong. Many new trees often grow on sandbars, where the soil is rich and wet.
Uses of the River Birch
Even though it naturally grows in wet ground, the River Birch can also grow on higher land. Its unique bark makes it a popular choice for planting in gardens and parks. Some types of River Birch have much whiter bark than the wild ones. These are special because they are resistant to a pest called the bronze birch borer, which can harm other white-barked birches in warmer areas.
Long ago, Native Americans used the boiled sap of the River Birch as a sweetener, similar to maple syrup. They also ate the inner bark as a survival food. The wood of the River Birch is not usually used for commercial lumber because it can be knotty. However, its strong wood is sometimes used to make local furniture, wooden items, and as fuel.
Many animals use the River Birch. Birds like waterfowl, ruffed grouse, and wild turkeys use it. Waterfowl often build their nests in its branches. Ruffed grouse and wild turkeys eat its seeds. Deer have also been known to nibble on young trees or branches they can reach.
Images for kids
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |








