Blocking (stage) facts for kids

In theatre, blocking is all about where actors stand and move on a stage during a performance. Think of it like a director drawing a map for the actors! It makes sure everyone is in the right spot for the audience to see them and for the story to make sense.
The idea of blocking started in the 1800s. Back then, theatre directors would use tiny wooden blocks on a small model stage to plan out where each actor should go. Today, directors usually figure out the blocking during rehearsal. They tell the actors exactly where to move. This helps create the right dramatic effect and makes sure the lighting looks good. It also ensures that the audience can see everything important happening on stage.
Contents
Understanding the Stage Areas
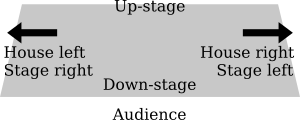
To help with blocking, different parts of the stage have special names. These names help directors and actors understand directions clearly.
Upstage and Downstage
- The very back of the stage, farthest from the audience, is called upstage.
- The front of the stage, closest to the audience, is called downstage.
These names come from old theatres where the stage was often built on a slight slope. The back of the stage was higher (up) and the front was lower (down).
Stage Left and Stage Right
- Stage left and stage right are always from the actor's point of view. If an actor is standing on stage facing the audience, their left side is stage left, and their right side is stage right.
House Left and House Right
- House left and house right are from the audience's point of view. If you are sitting in the audience looking at the stage, your left side is house left, and your right side is house right. It's important not to mix these up!
Images for kids
 | John T. Biggers |
 | Thomas Blackshear |
 | Mark Bradford |
 | Beverly Buchanan |