Velvet boronia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Velvet boronia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Boronia hippopala in the Royal Tasmanian Botanical Gardens | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
 |
|
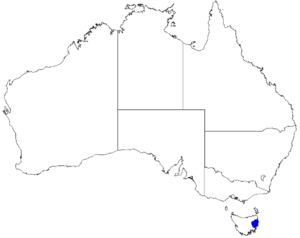
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium |
The Velvet Boronia (scientific name: Boronia hippopala) is a special plant. It belongs to the citrus family, called Rutaceae. This plant is found only in Tasmania, which means it's endemic there. It grows as a straight, woody bush with leaves that look like feathers. Its flowers are white to pink and have four petals.
Contents
What Does Velvet Boronia Look Like?
The Velvet Boronia is a woody shrub that stands upright. It can grow up to about 1.5 m (5 ft) tall. Its branches and leaves are covered with tiny hairs, giving it a soft, "velvet" feel.
Its leaves are interesting because they have smaller parts called leaflets. Each leaf has three, five, or seven leaflets. The whole leaf is about 6–10 mm (0.2–0.4 in) long and 6–14 mm (0.2–0.6 in) wide. The stem that holds the leaf is called a petiole and is about 2–3 mm (0.08–0.1 in) long. The leaflet at the very end is narrow, about 1–4 mm (0.04–0.2 in) long and 1–2 mm (0.04–0.08 in) wide. The side leaflets are similar but a bit longer.
The flowers of the Velvet Boronia are white to pink. They grow either alone or in small groups of up to three. These groups appear where the leaves meet the stem, which is called the leaf axil. The small stalk holding the flower group is a peduncle, only about 1 mm (0.04 in) long.
Each flower has four narrow, triangular sepals. These are small leaf-like parts that protect the flower bud. They are about 1–2 mm (0.04–0.08 in) long. The four petals are the colorful parts of the flower, measuring about 3.5–4.5 mm (0.1–0.2 in) long. Inside the flower, there are eight stamens, which are the parts that produce pollen. These stamens are hairy.
Velvet Boronia flowers bloom from October to January. After flowering, the plant produces a fruit. This fruit is a small capsule, about 2.5 mm (0.1 in) long and 1.5 mm (0.06 in) wide.
How Velvet Boronia Got Its Name
The scientific name Boronia hippopala was officially given to this plant in 2003. A scientist named Marco F. Duretto described it in a science journal called Muelleria. He studied a plant sample found on Mount Arthur.
The second part of its scientific name, hippopala, is interesting. It is thought to come from Latin words. "Hippo" means "horse" and "palus" means "marsh." This name might refer to where the plant usually grows, which is often in wet, marshy areas. However, some experts say the ancient Greek word hippos (ἵππος) also means "horse."
Where Does Velvet Boronia Live?
The Velvet Boronia prefers to grow in wet areas. You can find it in wet heathlands or scrublands. It is only known to exist in three specific places. All these places are near the St Pauls River in northern Tasmania.
Protecting the Velvet Boronia
The Velvet Boronia is considered a "vulnerable" species. This means it is at risk of disappearing if we don't protect it. Both the Australian government and the Tasmanian government have laws to protect it. These laws are the Commonwealth Government Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 (EPBC) Act and the Tasmanian Government Threatened Species Protection Act 1995.
There are a few main dangers to the Velvet Boronia:
- Dieback disease: A disease caused by a type of water mold called Phytophthora cinnamomi can make the plant sick and die.
- Fire: Fires that happen too often or at the wrong time can harm the plant's natural growth cycle.
- Water changes: Changes in how water flows in its habitat can also threaten the plant.


