Boshin War facts for kids
The Boshin War (pronounced "Bo-shin"), also called the Japanese Revolution, was a big fight in Japan. It was a civil war, meaning people from the same country fought each other. This war happened from 1868 to 1869.
On one side were the forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate. The Shogunate was like a military government that had ruled Japan for over 250 years. On the other side were people who wanted to bring back the power of the Emperor. They wanted the Emperor to be the true leader of Japan again. This change was called the Meiji Restoration.
Contents
What Was the Boshin War?
The Boshin War was a conflict that changed Japan forever. It marked the end of the samurai era and the start of modern Japan. The war led to big changes in how the country was run and how it interacted with the rest of the world.
Why Did the War Start?
For a long time, Japan was ruled by the Tokugawa Shogunate. The Emperor was respected, but he didn't have much real power. By the mid-1800s, many people in Japan felt it was time for a change.
- Outside Pressure: Other countries, especially Western ones, wanted Japan to open its borders for trade. The Shogunate struggled to deal with this pressure.
- Desire for Change: Some powerful areas in Japan, like Satsuma and Chōshū, believed the Shogunate was weak. They wanted to make Japan stronger and more modern.
- Restoring the Emperor: These groups believed that giving power back to the Emperor would unite Japan. They thought this would help Japan stand up to foreign countries.
Who Fought in the War?
The war was mainly fought between two sides:
- Shogunate Forces: These were loyal to the Tokugawa Shogunate. They included many traditional samurai warriors.
- Imperial Forces: These groups supported the Emperor. They came from powerful areas like Satsuma, Chōshū, and Tosa. They often had more modern weapons and training.
The End of the Shogunate
The Imperial forces, with their modern weapons and strong desire for change, slowly gained the upper hand.
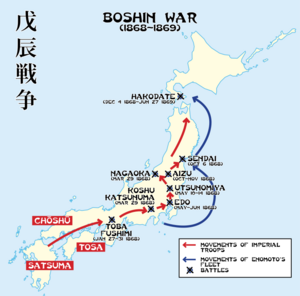
- Battle of Toba-Fushimi: This was one of the first major battles. It took place near Kyoto in early 1868. The Imperial forces won, showing their strength.
- March to Edo: After this victory, the Imperial army marched towards Edo (modern-day Tokyo). Edo was the Shogunate's capital.
- Surrender of Edo: The Shogun's forces eventually surrendered Edo without a major fight. This was a big step towards ending the Shogunate.
The Final Battles
Even after Edo fell, some Shogunate loyalists continued to fight.
- Northern Resistance: Some groups in northern Japan formed an alliance against the Imperial forces. They fought several battles.
- Republic of Ezo: The last stand was on the northern island of Hokkaido. Some Shogunate supporters set up a short-lived republic there.
- Battle of Hakodate: This was the final battle of the war. It took place in Hokkaido in 1869. The Imperial forces won, ending the conflict.
What Happened After the War?
The Boshin War officially ended the Tokugawa Shogunate. The Emperor Meiji was now the true ruler of Japan.
- Meiji Restoration: This period of change began. Japan quickly modernized its army, navy, and government.
- End of Samurai: The samurai class was abolished. This meant samurai no longer had their special status.
- Modern Japan: Japan became a powerful, modern nation. It quickly caught up with Western countries.
The Boshin War was a turning point in Japanese history. It led to a new era of rapid change and growth for the country.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra Boshin para niños
In Spanish: Guerra Boshin para niños
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |