CAPTCHA facts for kids
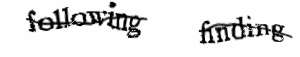
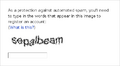
A CAPTCHA is a special test you often see online. It helps websites figure out if you are a real person or a computer program (sometimes called a "bot"). CAPTCHA stands for "Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart." It's like a mini-quiz that humans can easily solve, but computers find very difficult.
You might see a CAPTCHA when you are signing up for a new account, posting a comment, or buying tickets online. Its main job is to stop robots from doing things like creating lots of fake accounts, sending out spam messages, or trying to guess passwords. The idea for CAPTCHA comes from the work of a famous mathematician named Alan Turing, who created the "Turing test" to see if a machine could think like a human.
Contents
What is a CAPTCHA?
A CAPTCHA is designed to be easy for humans but hard for machines. This is because computers are very good at following instructions, but they struggle with things that require human-like understanding, like reading distorted text or recognizing objects in pictures.
How Does a CAPTCHA Work?
Most CAPTCHAs ask you to do something simple. This could be:
- Typing letters or numbers that are twisted, blurry, or have lines through them.
- Clicking on specific objects in a picture, like all the squares that show a bicycle.
- Solving a very simple math problem.
- Listening to an audio clip and typing what you hear.
Because computer programs aren't as good as humans at these tasks, they usually fail the CAPTCHA. This helps websites keep out unwanted automated activity.
Why Do We Need CAPTCHAs?
CAPTCHAs play an important role in keeping the internet safe and fair for everyone. Without them, websites would face many problems.
Stopping Spam and Fake Accounts
One of the biggest reasons for CAPTCHAs is to prevent spam. Spammers use bots to create thousands of fake email accounts or post unwanted messages on websites. CAPTCHAs make it much harder for these bots to get through. This means you get less junk mail and websites stay cleaner.
Protecting Online Security
CAPTCHAs also help protect your online accounts. For example, some bots try to guess passwords very quickly. A CAPTCHA can slow them down or stop them completely by asking for a human check after a few failed attempts. This adds an extra layer of security to your information.
Ensuring Fair Access
Sometimes, popular events like concert tickets or limited-edition items go on sale. Bots might try to buy up all the tickets or items very quickly, making it unfair for real people. CAPTCHAs help ensure that actual humans have a chance to get these things.
Types of CAPTCHAs
Over the years, different kinds of CAPTCHAs have been developed. Each one tries to find new ways to tell humans and bots apart.
Text-Based CAPTCHAs
These are the most common type. They show you a picture of distorted text, and you have to type what you see into a box. The letters might be:
- Twisted or rotated.
- Overlapping.
- Hidden behind lines or dots.
- Made with different colors or fonts.
The goal is to make it hard for a computer to "read" the text, but still readable for a human.
Image-Based CAPTCHAs
These CAPTCHAs ask you to identify objects in pictures. For example, you might see a grid of nine images and be asked to:
- "Select all squares with traffic lights."
- "Click on all images that show a bridge."
This type of CAPTCHA relies on a computer's difficulty in understanding the content of an image as well as a human can.
Audio CAPTCHAs
For people who have trouble seeing the visual CAPTCHAs, there are audio versions. You can listen to a distorted audio clip of letters or numbers and then type what you hear.
No CAPTCHA reCAPTCHA
You might have seen a checkbox that says "I'm not a robot." This is a newer type of CAPTCHA from Google called reCAPTCHA. It often doesn't even require you to solve a puzzle. Instead, it uses advanced technology to analyze your mouse movements, browsing history, and other factors to decide if you're a human. If it's not sure, then it might give you a visual puzzle to solve.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Captcha para niños
In Spanish: Captcha para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |